Page 79 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 79
Core network aspects 1
The operational procedures of the scenario are as follows:
1) User A requests an execution of NDO-func (data-processing function) from its service provider
(labelled Service provider-1 in Figure 7-15). The name of NDO-func is accompanied by that of
NDO-data_in.
2) To execute NDO-func, Service provider-1 requests NDO-data_in from its service provider (Service
provider-2).
3) Service provider-1 receives NDO-data_in from Service provider-2. Then, it executes NDO-func with
NDO-data_in, and produces NDO-data_out (output data: result of the execution).
4) While NDO-data_out is downloaded from service provider-1 to User A, it can be stored on selected
DAN elements along the downloading path. In addition, NDO-func can be pushed to selected DAN
elements or pulled by other DAN elements when it is necessary.
5) User B requests an execution of NDO-func which specifies NDO-data_in as an input to the service
provider. At this time, the request hits the cached NDO-data_out on the DAN element.
6) Since NDO-data_out is the result of the processing function NDO-func acting on NDO-data_in, it is
directly served from the DAN element, not from the service provider.
7) User C requests an execution of NDO-func that specifies NDO-data_in as an input to the service
provider. At this time, the request hits the cached NDO-func on the DAN element.
8) Thus, the DAN element only requests NDO-data_in (omitted in Figure 7-15) to Service provider-2.
Then, it executes NDO-func as an input NDO-data_in, produces NDO-data_out, and finally delivers
it to User C.
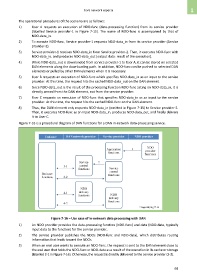
Figure 7-16 is a procedural diagram of DAN functions for a DAN in-network data-processing service.
Figure 7-16 – Use case of in-network data processing with DAN
1) An NDO provider provides the data-processing function (NDO-func) and data (NDO-data, typically
input data to the function) for the service provider.
2) The service provider publishes the NDOs (NDO-func and NDO-data), which distributes routing
information that leads toward the NDOs.
3) When an end user wants to execute an NDO-func, the request is sent to the DAN element close to
the end user that holds the NDO-func or NDO-data as a result of the execution in its cache or storage
(labelled 3-1 in Figure 7-16). Otherwise, the request is directly delivered to the service provider (3-2).
69