Page 469 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 469
Core network aspects 1
8. The IP sends its availability and capability to the PAM-SCP.
9. The PAM-SCP instructs the IP to send "Info request (called address)" (in FSK) to the AP.
10. The "Info request (called address)" message is sent from the IP to the AP.
11. The AP replies with the "called address" (in FSK).
12. The IP sends the received called address to the PAM-SCP.
13. The PAM-SCP indicates to the (MSC/VLR)/SSP to release the bearer connection with the IP.
14. The (MSC/VLR)/SSP sends the release to the IP.
15. The IP responds with a release complete confirmation.
16. The PAM-SCP processes the origination according to the user's service subscription (the user profile
was stored on PAM-SCP during the registration phase) and sets up the connection with the called
party.
17. The (MSC/VLR)/SSP sends the call set-up request to the called party, with the subsequent call
handling being the same as normal IN service handling.
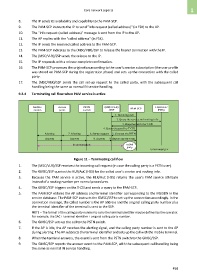
9.3.4 Terminating call flow when PAM service is active
Mobile Access PSTN (MSC/VLR) HLR/AuC
station point switch /SSP PAM-SCP (HSS)
1. Incoming call
2. Query the service and routing info
3. Response with the T-CSI
4. Query triggered by T-CSI
Alerting 7. Alerting 6. Set up request- 5. Connect via PSTN
Answer Answer 8. Answer 9. Report answer event
In conversation called
party
Q.1763/Y.2803(07)_F11
Figure 11 – Terminating call flow
1. The (MSC/VLR)/SSP receives the incoming call request (in case the calling party is a PSTN user).
2. The GMSC/SSP queries the HLR/AuC (HSS) for the called user's service and routing info.
3. Because the PAM service is active, the HLR/AuC (HSS) returns the user's PAM service attribute
instead of a routing number per normal procedures.
4. The GMSC/SSP triggers on the T-CSI and sends a query to the PAM-SCP.
5. The PAM-SCP obtains the AP address and terminal identifier corresponding to the MSISDN in the
service database. The PAM-SCP instructs the GMSC/SSP to set-up the connection accordingly. In the
connection message, the called number is the AP address and the original calling party number plus
the terminal identifier of the terminal is sent to the SSP.
NOTE – The format of the calling party number to carry the terminal identifier may be defined by the operator.
For example, the SAC + terminal identifier + original calling party number.
6. The GMSC/SSP sets up the call to the PSTN switch.
7. If the AP is idle, the AP receives the alerting signal, and the calling party number is sent to the AP
during alerting. The AP subtracts the terminal identifier and sets up the call with the mobile terminal.
8. When the terminal answers, the event is sent from the PSTN switch to the GMSC/SSP.
9. The GMSC/SSP reports the answer event to the PAM-SCP, with the subsequent call handling being
the same as normal IN service handling.
459