Page 468 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 468
1 Core network aspects
12. The "Deregistration response" message is sent from the IP to the AP, and the AP sends the
deregistration response to the terminal in the wireless protocol if the terminal is still accessible.
13. After finishing the sending of information in-band to the AP, the IP sends to the PAM-SCP the result.
14a. The PAM-SCP indicates to the (MSC/VLR)/SSP to release the bearer connection with the IP.
15a. The (MSC/VLR)/SSP sends the release to the IP.
16a. The IP responds with release complete confirmation.
14b. When the AP receives the registration response, the AP ends the registration by releasing the call.
15b. The release call message is sent to the (MSC/VLR)/SSP.
16b. The (MSC/VLR)/SSP ends with the release complete confirmation.
17. The (MSC/VLR)/SSP reports the release event to the PAM-SCP.
18. The PAM-SCP finishes the dialogue with the (MSC/VLR)/SSP.
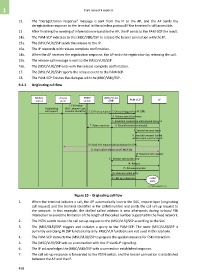
9.3.3 Originating call flow
Mobile Access PSTN (MSC/VLR)
station point switch /SSP PAM-SCP IP
1. Call setup
Originating (SAC, request type,
call request terminal identifier) 2. Call setup request 3. Query (triggered by N-CSI)
4. Prepare special resource
5. Establish connection with special resource
7. Setup response 6. Special resource connected
8. Special resource ready
9. Send info request (called
address) and wait for result
10. Send info request (called address) in FSK
11. Send called address in DTMF/FSK
12. Result of info request
13. Release special resource
14. Release
15. Release complete
16. Connect called party
17. Set up connection called
party
Q.1763/Y.2803(07)_F10
Figure 10 – Originating call flow
1. When the terminal initiates a call, the AP automatically inserts the SAC, request type (originating
call request) and the terminal identifier in the called number and sends the call set-up request to
the network. In this example, the dialled called address is sent afterwards during in-band FSK
interaction to avoid the limitation of the length of the called number supported in the fixed network.
2. The PSTN switch routes the call set-up request to the (MSC/VLR)/SSP according to the SAC.
3. The (MSC/VLR)/SSP triggers and initiates a query to the PAM-SCP. The node (MSC/VLR)/SSP is
currently exercising IN SSP functionality only. MSC/VLR functions are not used in this scenario.
4. The PAM-SCP instructs the (MSC/VLR)/SSP to prepare the special resource for FSK interaction.
5. The (MSC/VLR)/SSP sets up a connection with the IP via ISUP signalling.
6. The IP acknowledges the (MSC/VLR)/SSP with a connection established response.
7. The call set-up response is forwarded to the PSTN switch, and the bearer connection is established
between the AP and the IP.
458