Page 94 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 94
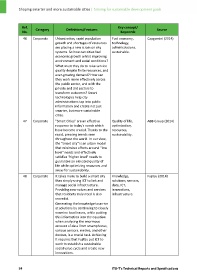
Ref. Category Definitions/Features Key concept/ Source
No. Keywords
46 Corporate Urbanization, rapid population Fuel economy, Capgemini (2014)
growth and shortages of resources technology,
are placing a new strain on city administrations,
systems. So how can cities fuel sustainable.
economic growth whilst improving
environment and social conditions?
What must they do to raise service
quality despite finite resources, and
ever‐growing demand? How can
they work more effectively across
the public sector, and with the
private and 3rd sectors to
transform outcomes? Smart
technologies help city
administrations tap into public
information and create not just
smarter, but more sustainable
cities.
47 Corporate "Smart Cities" are an effective Quality of life, ABB Group (2014)
response to today's needs which optimization,
have become crucial. Thanks to the resources,
rapid, pressing trends seen sustainability.
throughout the world. In our view,
the "smart city" is an urban model
that minimizes efforts around "low
level" needs and effectively
satisfies "higher level" needs to
guarantee an elevated quality of
life while optimizing resources and
areas for sustainability.
48 Corporate It takes more to build a smart city Knowledge, Fujitsu (2014)
than simply using ICT to link and solutions, sensors,
manage social infrastructure. data, ICT,
Providing new values and services innovations,
that residents truly need is also infrastructure.
essential.
Generating the knowledge to arrive
at solutions by continuing to closely
examine local issues, while putting
this information into the equation
when analysing the enormous
amount of data from smartphones,
various sensors, metres, and other
devices, is a crucial task. Achieving
it requires that Fujitsu put ICT to
work to establish a sustainable
social value cycle and create new
innovations.
84 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications