Page 814 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 814
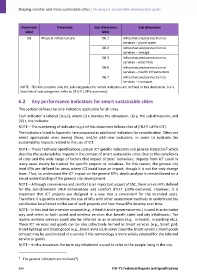
Dimension Dimension Sub‐dimension Sub‐dimension
label label
D6 Physical infrastructure D6.1 Infrastructure/connection to
services – piped water
D6.2 Infrastructure/connection to
services – sewage
D6.3 Infrastructure/connection to
services – electricity
D6.6 Infrastructure/connection to
services – health infrastructure
D6.7 Infrastructure/connection to
services – transport
NOTE ‐ This list contains only the sub‐categories for which indicators are defined in this document. For a
total set of sub‐categories, refer to [ITU‐T L.KPIs‐overview].
6.2 Key performance indicators for smart sustainable cities
This section defines the core indicators applicable for all cities.
Each indicator is labeled (Ix.y.z), where (i) x denotes the dimension, (ii) y, the sub‐dimension, and
(iii) z, the indicator.
NOTE – The numbering of indicator Ix,y,z of this document follows that of [ITU‐T L.KPIs‐ICT].
The indicators listed in Appendix I are proposed as additional indicators for consideration. Cities can
select appropriate ones among those, and/or add new indicators, in order to evaluate the
sustainability impacts related to the use of ICT.
2
NOTE – These Technical Specifications contain ICT specific indicators and general indicators which
describe the sustainability impacts in the context of smart sustainable cities. Due to the complexity
of cites and the wide range of factors that impact citizens´ behaviour, impacts from ICT could in
many cases mainly be tracked for specific projects or initiatives. For this reason, the general city
level KPIs are defined for areas where ICT could have an impact, though it is not the only change
lever. Thus, to understand the ICT impact on the general KPIs, depth analysis is needed based on a
broad understanding of the general city development.
NOTE – Although convenience and comfort is an important aspect of SSC, there are no KPIs defined
for the sub‐dimension D4.4 Convenience and comfort [ITU‐T L.KPIs‐overview]. However, it is
important that ICT projects are designed in a way that is convenient for the intended users.
Therefore it is good to combine the use of KPIs with other assessment methods to understand the
satisfaction level linked to the use of such projects and how these KPIs develop over time.
NOTE – In this text the e‐service concept (e.g., e‐health and e‐governance etc.) is used in an inclusive
way and refers to both wired and wireless services that benefit cities and city inhabitants. The
mobile wireless services could also be referred to as m‐services (e.g., m‐health, m‐banking etc.).
These ICT services and goods can be also collectively termed as Smart services (e.g., Smart grid,
Smart lighting) and Smart goods (e.g., Smart meters). In some cases the Smart service / smart goods
concept may be used instead of e‐service if this terminology is more widely adopted for the referred
service or goods.
NOTE – In this document the term city inhabitant is used to refer to the people living in the city.
2 The general indicators are marked (*).
804 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications