Page 238 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 238
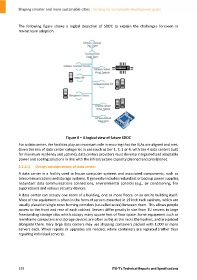
The following figure shows a logical depiction of SDDC to explain the challenges foreseen in
mainstream adoption.
Figure 8 – A logical view of future SDDC
For a data center, the facilities play an important role in ensuring that the SLAs are aligned and met.
Given the mix of data center categories in use (such as tier 1, 2, 3 or 4, with tier 4 data centers built
for maximum resiliency and uptime), data centers providers must develop integrated and adaptable
power and cooling solutions in line with the infrastructure capacity planned and provisioned.
2.1.1.3 Design considerations of data center
A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as
telecommunications and storage systems. It generally includes redundant or backup power supplies,
redundant data communications connections, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire
suppression) and various security devices.
A data center can occupy one room of a building, one or more floors, or an entire building itself.
Most of the equipment is often in the form of servers mounted in 19 inch rack cabinets, which are
usually placed in single rows forming corridors (so‐called aisles) between them. This allows people
access to the front and rear of each cabinet. Servers differ greatly in size from 1U servers to large
freestanding storage silos which occupy many square feet of floor space. Some equipment such as
mainframe computers and storage devices are often as big as the racks themselves, and are placed
alongside them. Very large data centers may use shipping containers packed with 1,000 or more
servers each. When repairs or upgrades are needed, whole containers are replaced (rather than
repairing individual servers).
228 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications