Page 231 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 231
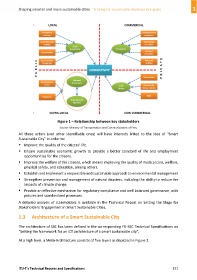
Figure 1 – Relationship between key stakeholders
Source: Ministry of Transportation and Communications of Peru
All these actors (and other identifiable ones) will have interests linked to the idea of "Smart
Sustainable City" in order to:
Improve the quality of the citizens' life.
Ensure sustainable economic growth to provide a better standard of life and employment
opportunities for the citizens.
Improve the welfare of the citizens, which means improving the quality of medical care, welfare,
physical safety, and education, among others.
Establish and implement a responsible and sustainable approach to environmental management.
Strengthen prevention and management of natural disasters, including the ability to reduce the
impacts of climate change.
Provide an effective mechanism for regulatory compliance and well balanced governance, with
policies and standardized processes.
A detailed analysis of stakeholders is available in the Technical Report on Setting the Stage for
Stakeholders’ Engagement in Smart Sustainable Cities.
1.3 Αrchitecture of a Smart Sustainable City
The architecture of SSC has been defined in the corresponding FG‐SSC Technical Specifications on
“Setting the framework for an ICT architecture of a smart sustainable city”,
At a high level, a Meta‐Architecture consists of five layers as depicted in Figure 2.
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 221