Page 101 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 101
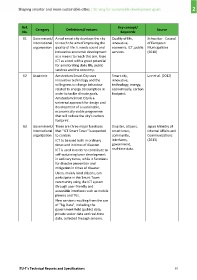
Ref. Category Definitions/Features Key concept/ Source
No. Keywords
61 Government/ A real smart city develops the city Quality of life, Schweiker ‐ Council
International to reach the aim of improving the innovative, of European
organization quality of life. It needs sound and economic, ICT, public Municipalities
innovative economic development services. (2010)
as a means to reach this aim. Uses
ICT as a tool with a great potential
for ameliorating daily life, public
services and the economy.
62 Academic Amsterdam Smart City uses Smart city, Lee et al. (2012)
innovative technology and the innovative,
willingness to change behaviour technology, energy,
related to energy consumption in economically, carbon
order to tackle climate goals. footprint.
Amsterdam Smart City is a
universal approach for design and
development of a sustainable,
economically viable programme
that will reduce the city's carbon
footprint.
63 Government/ There are three major functions Disaster, citizens, Japan Ministry of
International that "ICT Smart Town" is expected smart town, Internal Affairs and
organization to contain. community, Communications
ICT to be used both in ordinary interfaces, (2013)
times and in times of disaster. government,
ICT is used in order to contribute to real‐time data.
self‐sustaining town development
in ordinary times, while it functions
for disaster prevention and
mitigation in times of disaster.
Users, mainly local citizens, can
participate in the Smart Town
community using the ICT system
through user‐friendly and
accessible interfaces such as mobile
phones and TVs.
New services resulting from the use
of "Big Data", including the
government‐held (public) data,
private sector data and real‐time
data, collected through sensors.
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 91