Page 37 - ITU Kaleidoscope 2016
P. 37
ICTs for a Sustainable World
1. Someone in the organisation should take the initiative.
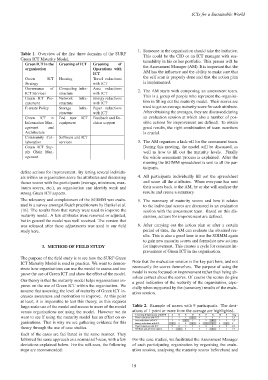
Table 1. Overview of the first three domains of the SURF
This could be the CIO or an ICT manager with sus-
Green ICT Maturity Model.
tainability in his or her portfolio. This person will be
Green ICT in the Greening of ICT Greening of the Assessment Manager (AM). It is important that the
organisation Operations with
AM has the influence and the ability to make sure that
ICT
the self scan is properly done and that the action plan
Green ICT Housing Travel reductions
Strategy with ICT is implemented.
Governance of Computing Infra- Area reductions 2. The AM starts with composing an assessment team.
ICT Services structure with ICT
Green ICT Pro- Network Infra- Energy reductions This is a group of people who represent the organisa-
curement structure with ICT tion in filling out the maturity model. Their scores are
used to get an average maturity score for each attribute.
E-waste Policy Storage Infra- Paper reductions
structure with ICT After obtaining the averages, they are discussed during
Green ICT in End user ICT Feedback and De- an evaluation session at which also a number of pos-
Information Man- equipment cision support sible actions for improvement are defined. To obtain
agement and good results, the right combination of team members
Architecture is crucial.
Community Col- Software and ICT
laboration services 3. The AM organises a kick-off for the assessment team.
Green ICT Sup- During this meeting, the model will be discussed, as
ply Chain Man- well as how to fill out the maturity levels. Finally
agement the whole assessment process is explained. After the
meeting the SGIMM spreadsheet is sent to all the par-
ticipants.
define actions for improvement. By letting several individu-
als within an organisation score the attributes and discussing 4. All participants individually fill out the spreadsheet
theses scores with the participants (average, minimum, max- and score all the attributes. When everyone has sent
imum scores, etc.), an organisation can identify weak and their scores back to the AM, he or she will analyse the
strong Green ICT aspects. results and create a summary.
The relevancy and completeness of the SGIMM was evalu- 5. The summary of maturity scores and how it relates
ated in a survey amongst Dutch practitioners by Hankel et al. to the individual scores are discussed in an evaluation
[16]. The results from that survey were used to improve the session with the assessment team. Based on this dis-
maturity model. A few attributes were removed or adjusted, cussion, actions for improvement are defined.
but in general the model was well received. The version that
was released after these adjustments was used in our field 6. After carrying out the action plan or after a certain
study here. period of time, the AM can evaluate the obtained res-
ults. This is also a good time to use the SGIMM again
to gain new maturity scores and formulate new actions
3. METHOD OF FIELD STUDY for improvement. This creates a cycle for constant im-
provement of Green ICT in the organisation.
The purpose of the field study is to see how the SURF Green
Note that the evaluation session is the key part here, and not
ICT Maturity Model is used in practice. We want to demon-
strate how organisations can use the model to assess and im- necessarily the scores themselves. The purpose of using the
model is more focused on improvement rather than being ab-
prove the use of Green ICT and show the effect of the model.
solute correct about the scores. Of course the scores do give
Our theory is that the maturity model helps organisations im-
a good indication of the maturity of the organisation, espe-
prove on the use of Green ICT within the organisation. We
cially when supported by the (summary) results of the evalu-
assume that assessing the level of maturity of Green ICT in- ation session.
creases awareness and motivation to improve. At this point
at least, it is impossible to test this theory, as this requires
large-scale use of the model and access to users of the model Table 2. Example of scores with 9 participants. The devi-
versus organisations not using the model. However we do ations of 1 point or more from the average are highlighted.
Greening of Operations with ICT A B C D E F G H I Avg
want to see if using the maturity model has an effect on or- Travel reductions with ICT 2 3 2 1 3 2 3 3 2 2,3
Area reductions with ICT 2 2 1 2 3 3 4 2 2 2,3
ganisations. That is why we are gathering evidence for this Energy reductions with ICT 1 2 2 3 2 1 4 2 1 2
theory through the use of case studies. Paper reductions with ICT 2 1 2 3 3 2 3 1 3 2 2 1 3 3 2 1 2 1 2,4
1,7
Feedback and decision support
Each of the cases are facilitated in the same manner. They
followed the same approach as a normal self-scan, with a few For the case studies, we facilitated the Assessment Manager
deviations explained below. For the self-scan, the following of each participating organisation by organising the evalu-
steps are recommended: ation session, analysing the maturity scores beforehand and
– 19 –