Page 66 - Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities: The Case of Dubai
P. 66
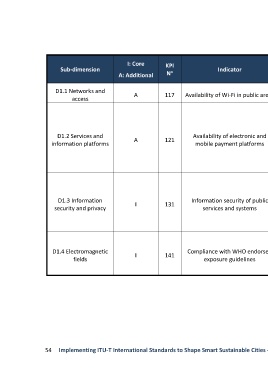
I: Core KPI
Sub-dimension o Indicator KPI definition KPI Analysis
A: Additional N
D1.1 Networks and A 117 Availability of Wi-Fi in public areas Number of (public) Wi-Fi hotspots at These KPIs indicate the presence
access certain points in the city. of Wi-Fi access in public areas and
the availability of mobile-payment
platforms. However these KPIs can
reflect access to these services on
Existence of public electronic and mobile a city level but not the level of
D1.2 Services and Availability of electronic and coverage of the service. Further
A 121 payment platforms to facilitate access to
information platforms mobile payment platforms evaluation of KPIs (in Dubai) over
city services for city inhabitants.
a period of several years will give
insights on its support to smart
city projects development.
Proportion of people who were victims This indicator determines Dubai’s
of incidents, due to illegal system access, diligence in the control and
unauthorized data storage or management of information
D1.3 Information Information security of public
I 131 transmission, unauthorized hardware security in public services and
security and privacy services and systems
and software modifications, which lead systems.
to information disclosure or financial
loss.
Application of WHO endorsed exposure This indicator reflects Dubai’s
guidelines for ICT installations in the city. application of EMF Standards for
D1.4 Electromagnetic I 141 Compliance with WHO endorsed NOTE – WHO endorsed exposure installation in cities.
fields exposure guidelines
guidelines are referred to in
(ITUT TR EMF Cons)
54 Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities – The Case of Dubai