Page 22 - Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016
P. 22
of copper networks in developing markets can – are investing in high-speed LTE-Advanced
make them unsuitable for investment. (LTE-A) networks, based on higher smartphone
7
penetration and the take-up of high-speed
Fixed incumbent operators in developed markets, streaming services. Figure 1.5 shows that
meanwhile, are more likely to adopt a gradualist 40 operators have launched or are planning
investment approach in order to leverage their various LTE-A deployments worldwide; 35 of these
copper network assets and introduce a mix of FTTx operators are in developed markets. The Republic
access approaches, including FTTH. In contrast to of Korea has one of the highest LTE penetration
incumbent operators, new market entrants are rates worldwide (at 66 per cent of connections in
deploying gigabit fibre networks in cities, as they 2014, and an expected 89 per cent by 2019) .
8
are not restricted by legacy investments in copper
networks. This is the case with Gigaclear and Other wireless network operators are investing in
CityFibre in the UK, and Google Fibre in the United public small cells, public Wi-Fi networks and in low
States and Africa. Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. Operators in developed
markets use public small-cell deployments to
address 3G and 4G network coverage and capacity
1.2.3 Wireless network investment trends deficits, particularly in city business districts where
the demand for data-hungry applications can be
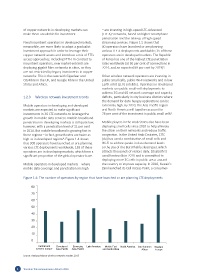
Mobile operators in developing and developed extremely high. By 2020, the Asia-Pacific region
markets are expected to make significant and North America will together account for
investments in 3G LTE networks to leverage the 78 per cent of the investment in public small cells .
9
growth in mobile data services. Mobile broadband
penetration in developing markets is still quite low, Mobile players in the Arab States also have been
however, with a penetration level of 21 per cent deploying small cells since 2010 to help alleviate
in 2014. But mobile broadband is growing fast in the strain on their networks and reduce traffic
these regions – in fact, growth rates are twice as congestion. In the United Arab Emirates, EITC
high as in developed regions . Figure 1.4 shows (du) has used a combination of small cells and
6
that 308 operators have launched or are planning Wi-Fi to address peaks in data demand levels
various LTE deployments worldwide; 138 of these at the site of the Burj Khalifa skyscraper, which
operators are in developing markets, which form a attracts thousands of visitors daily. Etisalat first
significant proportion of the global operator base. used femtocells in 2010 and is committed to
deploying more 3G cells in public areas around
Mobile operators in developed markets – where the country to improve capacity. In 2010, Kuwait’s
mobile data coverage and penetration are high Zain launched its Cell Access Point, a consumer-
Figure 1.4: The number of operators by region that have launched or are planning LTE deployments
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Central and Developed Emerging Latin America Middle East North America Sub-Saharan Western
Eastern Europe Asia-Pacific Asia-Pacific and North Africa Africa Europe
Source: Analysys Mason wireless networks tracker, 2015
4 Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016