Page 36 - AI Ready – Analysis Towards a Standardized Readiness Framework
P. 36
AI Ready – Analysis Towards a Standardized Readiness Framework
5 Data Analytics Strategy
In this section, we aim to derive an analytics strategy related to the different features corresponding
to each of the AI readiness factors. These features are derived from the “Detailed analysis of
the use cases and AI impacts on the use cases” described in Appendix A and “Specific impacts
of the characteristics of use cases on Standards Frameworks for AI readiness require further
study” described in Appendix B.
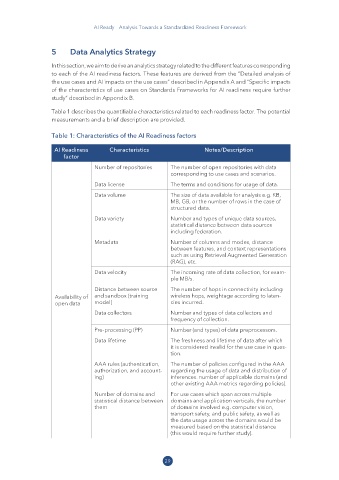
Table 1 describes the quantifiable characteristics related to each readiness factor. The potential
measurements and a brief description are provided.
Table 1: Characteristics of the AI Readiness factors
AI Readiness Characteristics Notes/Description
factor
Number of repositories The number of open repositories with data
corresponding to use cases and scenarios.
Data license The terms and conditions for usage of data.
Data volume The size of data available for analysis e.g. KB,
MB, GB, or the number of rows in the case of
structured data.
Data variety Number and types of unique data sources,
statistical distance between data sources
including federation.
Metadata Number of columns and modes, distance
between features, and context representations
such as using Retrieval Augmented Generation
(RAG), etc.
Data velocity The incoming rate of data collection, for exam-
ple MB/s.
Distance between source The number of hops in connectivity including
Availability of and sandbox (training wireless hops, weightage according to laten-
open data model) cies incurred.
Data collectors Number and types of data collectors and
frequency of collection.
Pre-processing (PP) Number (and types) of data preprocessors.
Data lifetime The freshness and lifetime of data after which
it is considered invalid for the use case in ques-
tion.
AAA rules (authentication, The number of policies configured in the AAA
authorization, and account- regarding the usage of data and distribution of
ing) inferences. number of applicable domains (and
other existing AAA metrics regarding policies).
Number of domains and For use cases which span across multiple
statistical distance between domains and application verticals, the number
them of domains involved e.g. computer vision,
transport safety, and public safety, as well as
the data usage across the domains would be
measured based on the statistical distance
(this would require further study).
29