Page 59 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2022
P. 59
Extended reality – How to boost quality of experience and interoperability
3.2 Named data networking 4.2 Why use SRv6
A Named Data Network (NDN) is different from IP SRv6 is a segment routing technology implemented using
networks by the mechanism of addressing a specific node by the IPv6 protocol, which is designed based on the concept of
IP address for the purpose of acquiring specific data or source routing. Therefore, packets can decide their routing
functions. Consumers pull the corresponding data or paths at the ingress, which is used to support traffic
functions by sending interest packets to the network, and engineering in IPv6 networks [16]. The prerequisite of
thus they can naturally adapt to scenarios where multiple performing load balancing for multiple computing service
computing nodes provide the same service and provide instances sharing the same anycast address through the
seamless mobility [12]. In addition, the Content Store (CS) network is that the service request packets sent by the user
in the NDN architecture can also provide reuse of terminal with the anycast address as the destination address
computational results. However, it is difficult to implement through the user plane of the network can be forwarded to a
in a practical deployment environment since NDN requires a suitable computing service instance. As a result, underlay
lot of modifications to the existing IP network and lacks a traffic engineering is the basis for anycast of overlay services
push mechanism. and the flexibility provided by SRv6 and the good affinity
with IP networks are the reasons why the SRv6 protocol is
3.3 Anycast proxy chosen as the underlay traffic engineering protocol.
IETF [13] defines the IPv6 addressing architecture, which 4.3 Architecture design
covers the definition and usage of IPv6 anycast addresses.
However, because IP anycast is difficult to support session- This paper draws on the design ideas of the anycast proxy
based stateful upper-layer services, and the rapidly changing and Dyncast, and improves it with the SRv6 protocol to
anycast members make the routing table unstable, the support service resource discovery, QoE-oriented service
anycast protocol is only widely used in single-round-trip instance selection and seamless mobility. The following is
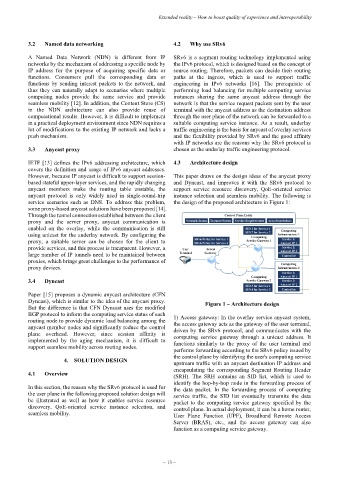
service scenarios such as DNS. To address this problem, the design of the proposed architecture in Figure 1:
some proxy-based anycast solutions have been proposed [14].
Through the tunnel connection established between the client
proxy and the server proxy, anycast communication is
enabled on the overlay, while the communication is still
using unicast for the underlay network. By configuring the
proxy, a suitable server can be chosen for the client to
provide services, and this process is transparent. However, a
large number of IP tunnels need to be maintained between
proxies, which brings great challenges to the performance of
proxy devices.
3.4 Dyncast
Paper [15] proposes a dynamic anycast architecture (CFN
Dyncast), which is similar to the idea of the anycast proxy. Figure 1 – Architecture design
But the difference is that CFN Dyncast uses the modified
BGP protocol to inform the computing service status of each 1) Access gateway: In the overlay service anycast system,
routing node to provide dynamic load balancing among the the access gateway acts as the gateway of the user terminal,
anycast member nodes and significantly reduce the control driven by the SRv6 protocol, and communicates with the
plane overhead. However, since session affinity is computing service gateway through a unicast address. It
implemented by the aging mechanism, it is difficult to functions similarly to the proxy of the user terminal and
support seamless mobility across routing nodes. performs forwarding according to the SRv6 policy issued by
the control plane by identifying the user's computing service
4. SOLUTION DESIGN upstream traffic with an anycast destination IP address and
encapsulating the corresponding Segment Routing Header
4.1 Overview (SRH). The SRH contains an SID list, which is used to
identify the hop-by-hop node in the forwarding process of
In this section, the reason why the SRv6 protocol is used for the data packet. In the forwarding process of computing
the user plane in the following proposed solution design will service traffic, the SID list eventually transmits the data
be illustrated as well as how it enables service resource packet to the computing service gateway specified by the
discovery, QoE-oriented service instance selection, and control plane. In actual deployment, it can be a home router,
seamless mobility. User Plane Function (UPF), Broadband Remote Access
Server (BRAS), etc., and the access gateway can also
function as a computing service gateway.
– 13 –