Page 65 - Digital solutions for integrated city management and use cases: A U4SSC deliverable on city platforms
P. 65
Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are centralizing
privacy standards for users around the world. GDPR is designed to harmonize privacy laws across
Europe. In most cases, cities have not yet developed an appropriate cybersecurity plan at the local
level. However, while this may be an expensive process, it is a compulsory step as data must be
stored in a secured manner.
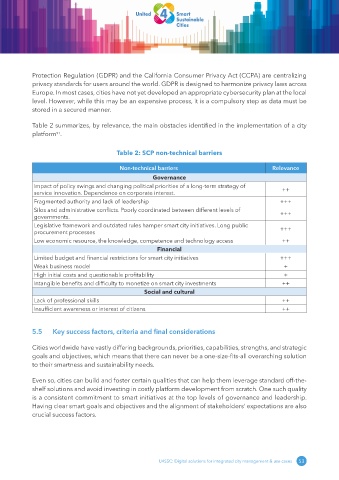
Table 2 summarizes, by relevance, the main obstacles identified in the implementation of a city
platform .
91
Table 2: SCP non-technical barriers
Non-technical barriers Relevance
Governance
Impact of policy swings and changing political priorities of a long-term strategy of ++
service innovation. Dependence on corporate interest.
Fragmented authority and lack of leadership +++
Silos and administrative conflicts. Poorly coordinated between different levels of +++
governments.
Legislative framework and outdated rules hamper smart city initiatives. Long public +++
procurement processes
Low economic resource, the knowledge, competence and technology access ++
Financial
Limited budget and financial restrictions for smart city initiatives +++
Weak business model +
High initial costs and questionable profitability +
Intangible benefits and difficulty to monetize on smart city investments ++
Social and cultural
Lack of professional skills ++
Insufficient awareness or interest of citizens ++
5.5 Key success factors, criteria and final considerations
Cities worldwide have vastly differing backgrounds, priorities, capabilities, strengths, and strategic
goals and objectives, which means that there can never be a one-size-fits-all overarching solution
to their smartness and sustainability needs.
Even so, cities can build and foster certain qualities that can help them leverage standard off-the-
shelf solutions and avoid investing in costly platform development from scratch. One such quality
is a consistent commitment to smart initiatives at the top levels of governance and leadership.
Having clear smart goals and objectives and the alignment of stakeholders’ expectations are also
crucial success factors.
U4SSC: Digital solutions for integrated city management & use cases 53