Page 45 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2021
P. 45
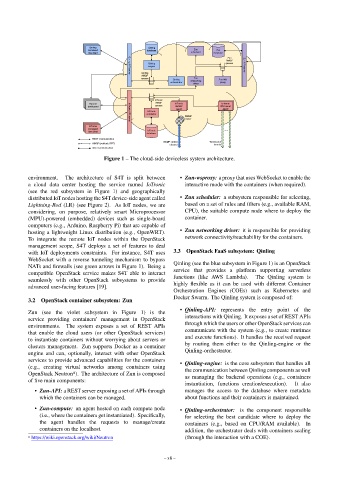
Qinling Qinling
command database Zun Zun
line client scheduler database
Zun
AMQP
Qinling queues Zun API server
engine
Qinling
Qinling API server
AMQP
queues Zun
Qinling networking Zun WS
orchestrator proxy
driver
IoTronic
Horizon AMQP IoTronic IoTronic
dashboard queues WAMP WS tunnel
agent agent
IoTronic
conductor
WAMP
router
IoTronic API server
IoTronic
command ...
line client IoTronic
database
REST communication
WAMP control WebSocket
AMQP (pub/sub, RPC)
channel tunnels
other communication
Figure 1 – The cloud-side deviceless system architecture.
environment. The architecture of S4T is split between • Zun-wsproxy: a proxy that uses WebSocket to enable the
a cloud data center hosting the service named IoTronic interactive mode with the containers (when required).
(see the red subsystem in Figure 1) and geographically
distributed IoT nodes hosting the S4T device-side agent called • Zun scheduler: a subsystem responsible for selecting,
Lightning-Rod (LR) (see Figure 2). As IoT nodes, we are based on a set of rules and filters (e.g., available RAM,
considering, on purpose, relatively smart Microprocessor CPU), the suitable compute node where to deploy the
(MPU)-powered (embedded) devices such as single-board container.
computers (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi) that are capable of
• Zun networking driver: it is responsible for providing
hosting a lightweight Linux distribution (e.g., OpenWRT).
network connectivity/reachability for the containers.
To integrate the remote IoT nodes within the OpenStack
management scope, S4T deploys a set of features to deal
with IoT deployments constraints. For instance, S4T uses 3.3 OpenStack FaaS subsystem: Qinling
WebSocket with a reverse tunneling mechanism to bypass
Qinling (see the blue subsystem in Figure 1) is an OpenStack
NATs and firewalls (see green arrows in Figure 1). Being a
service that provides a platform supporting serverless
compatible OpenStack service makes S4T able to interact
functions (like AWS Lambda). The Qinling system is
seamlessly with other OpenStack subsystems to provide
highly flexible as it can be used with different Container
advanced user-facing features [19].
Orchestration Engines (COEs) such as Kubernetes and
Docker Swarm. The Qinling system is composed of:
3.2 OpenStack container subsystem: Zun
• Qinling-API: represents the entry point of the
Zun (see the violet subsystem in Figure 1) is the
interactions with Qinling. It exposes a set of REST APIs
service providing containers’ management in OpenStack
through which the users or other OpenStack services can
environments. The system exposes a set of REST APIs
communicate with the system (e.g., to create runtimes
that enable the cloud users (or other OpenStack services)
and execute functions). It handles the received request
to instantiate containers without worrying about servers or
by routing them either to the Qinling-engine or the
clusters management. Zun supports Docker as a container
Qinling-orchestrator.
engine and can, optionally, interact with other OpenStack
services to provide advanced capabilities for the containers
• Qinling-engine: is the core subsystem that handles all
(e.g., creating virtual networks among containers using
the communication between Qinling components as well
OpenStack Neutron8). The architecture of Zun is composed
as managing the backend operations (e.g., containers
of five main components:
instantiation, functions creation/execution). It also
• Zun-API: a REST server exposing a set of APIs through manages the access to the database where metadata
which the containers can be managed. about functions and their containers is maintained.
• Zun-compute: an agent hosted on each compute node • Qinling-orchestrator: is the component responsible
(i.e., where the containers get instantiated). Specifically, for selecting the best candidate where to deploy the
the agent handles the requests to manage/create containers (e.g., based on CPU/RAM available). In
containers on the localhost. addition, the orchestrator deals with containers scaling
8 https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Neutron (through the interaction with a COE).
– xli –