Page 20 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 7 – Terahertz communications
P. 20
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 7
5 5 5
10 10 10
4 4 4
10 10 10
Capacity [Gbps] 10 3 2 Capacity [Gbps] 10 3 2 Capacity [Gbps] 10 3 2
10
10
10
WF: h = 1 km EP: h = 1 km WF: h = 1 km EP: h = 1 km
1 t t 1 WF: h = 1 km EP: h = 1 km 1
10 10 t t 10 t t
WF: h = 500 m EP: h = 500 m WF: h = 500 m EP: h = 500 m WF: h = 500 m EP: h = 500 m
t t t t t t
WF: h = 100 m EP: h = 100 m WF: h = 100 m EP: h = 100 m WF: h = 100 m EP: h = 100 m
t t t t t t
0 0 0
10 10 10
1 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 1 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 1 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Transmission distance (d) [m] Transmission distance (d) [m] Transmission distance (d) [m]
(a) Vertically‑up communication, = 0 . ∘ (b) Horizontal communication, = 90 . ∘ (c) Vertically‑down communication, = 180 . ∘
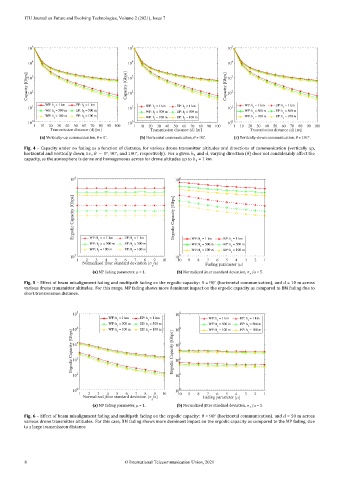
Fig. 4 – Capacity under no fading as a function of distance, for various drone transmitter altitudes and directions of communication (vertically up,
∘
∘
∘
horizontal and vertically down, i.e., = 0 , 90 , and 180 , respectively). For a given ℎ and , varying direction ( ) does not considerably affect the
capacity, as the atmosphere is dense and homogeneous across for drone altitudes up to ℎ = 1 km.
10 4 10 4
Ergodic Capacity [Gbps] Ergodic Capacity [Gbps]
WF: h = = 1 km
t
t
t
t
WF: h = = 500 m EP: h = 1 km WF: h = 1 km EP: h = 1 km
EP: h = 500 m
EP: h = 500 m
WF: h = 500 m
t t t t
WF: h = 100 m EP: h = 100 m WF: h = 100 m EP: h = 100 m
t t t t
3 3
10 10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Normalized jitter standard deviation [ /a] Fading parameter [ ]
s
(a) MP fading parameter, = 1. (b) Normalized jitter standard deviation, / = 5.
∘
Fig. 5 – Effect of beam misalignment fading and multipath fading on the ergodic capacity: = 90 (horizontal communication), and = 10 m across
various drone transmitter altitudes. For this range, MP fading shows more dominant impact on the ergodic capacity as compared to BM fading due to
short transmission distance.
10 5 10 5
WF: h = 1 km EP: h = 1 km WF: h = 1 km EP: h = 1 km
t t t t
WF: h = 500 m EP: h = 500 m WF: h = 500 m EP: h = 500 m
t t t t
4 WF: h = 100 m EP: h = 100 m 10 4 WF: h = 100 m EP: h = 100 m
10
Ergodic Capacity [Gbps] 10 3 2 Ergodic Capacity [Gbps] 10 3 2
t
t
t
t
10
10
10 1 10 1
10 0 10 0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Normalized jitter standard deviation [ /a] Fading parameter [ ]
s
(a) MP fading parameter, = 1. (b) Normalized jitter standard deviation, / = 5.
∘
Fig. 6 – Effect of beam misalignment fading and multipath fading on the ergodic capacity: = 90 (horizontal communication), and = 50 m across
various drone transmitter altitudes. For this case, BM fading shows more dominant impact on the ergodic capacity as compared to the MP fading, due
to a large transmission distance.
8 © International Telecommunication Union, 2021