Page 72 - A U4SSC deliverable - Guidelines on tools and mechanisms to finance Smart Sustainable Cities projects
P. 72
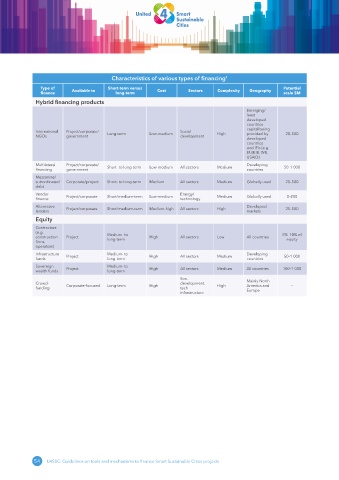
Characteristics of various types of financing 1
Type of Available to Short-term versus Cost Sectors Complexity Geography Potential
finance long-term scale $M
Hybrid financing products
Emerging/
least
developed
countries –
capital being
International Project/corporate/ Long-term Low-medium Social High provided by 20–500
NGOs government development
developed
countries
and IFIs (e.g.
EU/EIB, WB,
USAID)
Multilateral Project/corporate/ Short- to long-term Low-medium All sectors Medium Developing 50–1 000
financing government countries
Mezzanine/
subordinated Corporate/project Short- to long-term Medium All sectors Medium Globally used 20–500
debt
Vendor Project/corporate Short/medium-term Low-medium Energy/ Medium Globally used 0–200
finance technology
Alternative Project/corporate Short/medium-term Medium-high All sectors High Developed 25–500
lenders markets
Equity
Contractors
(e.g. Medium- to 5%–10% of
construction Project long-term High All sectors Low All countries equity
firms,
operators)
Infrastructure Project Medium- to High All sectors Medium Developing 50–1 000
funds long-term countries
Sovereign Project Medium- to High All sectors Medium All countries 100–1 000
wealth funds long-term
Soc.
Crowd- Corporate-focused Long-term High development, High Mainly North –
America and
funding tech Europe
infrastructure
54 U4SSC: Guidelines on tools and mechanisms to finance Smart Sustainable Cities projects