Page 18 - U4SSC Factsheet, Pully, Switzerland, June 2020
P. 18
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Infrastructure
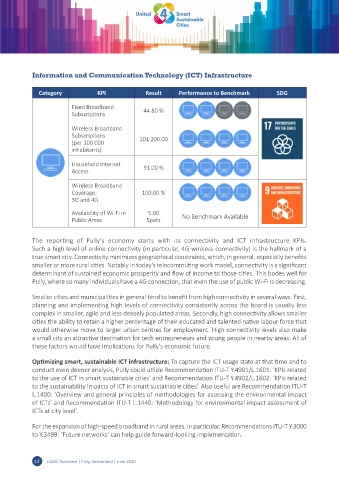
Category KPI Result Performance to Benchmark 4 SDG
Fixed Broadband 44.80 %
Subscriptions
Wireless Broadband
Subscriptions 101 200.00
(per 100 000
inhabitants)
Household Internet
Access 91.00 %
Wireless Broadband
Coverage: 100.00 %
3G and 4G
Availability of Wi-Fi in 5.00 No Benchmark Available
Public Areas Spots
The reporting of Pully's economy starts with its connectivity and ICT infrastructure KPIs.
Such a high level of online connectivity (in particular, 4G wireless connectivity) is the hallmark of a
true smart city. Connectivity minimizes geographical constraints, which, in general, especially benefits
smaller or more rural cities. Notably in today's telecommuting work model, connectivity is a significant
determinant of sustained economic prosperity and flow of income to those cities. This bodes well for
Pully, where so many individuals have a 4G connection, that even the use of public Wi-Fi is decreasing.
Smaller cities and municipalities in general tend to benefit from high connectivity in several ways. First,
planning and implementing high levels of connectivity consistently across the board is usually less
complex in smaller, agile and less densely populated areas. Secondly, high connectivity allows smaller
cities the ability to retain a higher percentage of their educated and talented native labour force that
would otherwise move to larger urban centres for employment. High connectivity levels also make
a small city an attractive destination for tech entrepreneurs and young people in nearby areas. All of
these factors would have implications for Pully’s economic future.
Optimizing smart, sustainable ICT infrastructure: To capture the ICT usage state at that time and to
conduct even deeper analysis, Pully could utilize Recommendation ITU-T Y.4901/L.1601: ‘KPIs related
to the use of ICT in smart sustainable cities’ and Recommendation ITU-T Y.4902/L.1602: ‘KPIs related
to the sustainability impacts of ICT in smart sustainable cities’. Also useful are Recommendation ITU-T
L.1400: ‘Overview and general principles of methodologies for assessing the environmental impact
of ICTs’ and Recommendation ITU-T L.1440: ‘Methodology for environmental impact assessment of
ICTs at city level’.
For the expansion of high-speed broadband in rural areas, in particular, Recommendations ITU-T Y.3000
to Y.3499: ‘Future networks’ can help guide forward-looking implementation.
12 U4SSC Factsheet | Pully, Switzerland | June 2020