Page 29 - U4SSC Blockchain for smart sustainable cities
P. 29
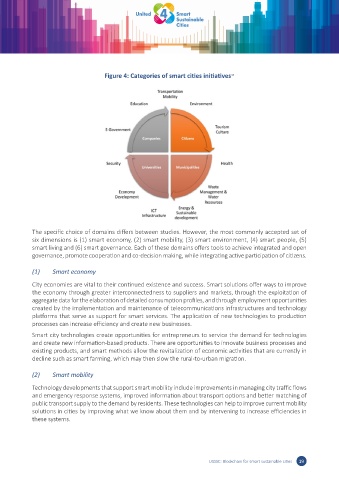
Figure 4: Categories of smart cities initiatives 44
The specific choice of domains differs between studies. However, the most commonly accepted set of
six dimensions is (1) smart economy, (2) smart mobility, (3) smart environment, (4) smart people, (5)
smart living and (6) smart governance. Each of these domains offers tools to achieve integrated and open
governance, promote cooperation and co-decision making, while integrating active participation of citizens.
(1) Smart economy
City economies are vital to their continued existence and success. Smart solutions offer ways to improve
the economy through greater interconnectedness to suppliers and markets, through the exploitation of
aggregate data for the elaboration of detailed consumption profiles, and through employment opportunities
created by the implementation and maintenance of telecommunications infrastructures and technology
platforms that serve as support for smart services. The application of new technologies to production
processes can increase efficiency and create new businesses.
Smart city technologies create opportunities for entrepreneurs to service the demand for technologies
and create new information-based products. There are opportunities to innovate business processes and
existing products, and smart methods allow the revitalization of economic activities that are currently in
decline such as smart farming, which may then slow the rural-to-urban migration.
(2) Smart mobility
Technology developments that support smart mobility include improvements in managing city traffic flows
and emergency response systems, improved information about transport options and better matching of
public transport supply to the demand by residents. These technologies can help to improve current mobility
solutions in cities by improving what we know about them and by intervening to increase efficiencies in
these systems.
U4SSC: Blockchain for smart sustainable cities 19