Page 163 - ITU Journal, Future and evolving technologies - Volume 1 (2020), Issue 1, Inaugural issue
P. 163
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 1 (2020), Issue 1
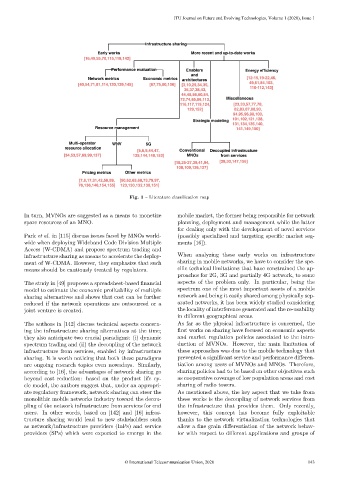
Fig. 1 – Literature classification map
In turn, MVNOs are suggested as a means to monetize mobile market, the former being responsible for network
spare resources of an MNO. planning, deployment and management while the latter
for dealing only with the development of novel services
Park et al. in [115] discuss issues faced by MNOs world- (possibly specialized and targeting specific market seg-
wide when deploying Wideband Code Division Multiple ments [16]).
Access (W-CDMA) and propose spectrum trading and
infrastructure sharing as means to accelerate the deploy- When analyzing these early works on infrastructure
ment of W-CDMA. However, they emphasize that such sharing in mobile networks, we have to consider the spe-
means should be cautiously treated by regulators. cific technical limitations that have constrained the ap-
proaches for 2G, 3G and partially 4G network, to some
The study in [49] proposes a spreadsheet-based financial aspects of the problem only. In particular, being the
model to estimate the economic profitability of multiple spectrum one of the most important assets of a mobile
sharing alternatives and shows that cost can be further network and being it easily shared among physically sep-
reduced if the network operations are outsourced or a arated networks, it has been widely studied considering
joint venture is created. the locality of interference generated and the re-usability
in different geographical areas.
The authors in [142] discuss technical aspects concern- As far as the physical infrastructure is concerned, the
ing the infrastructure sharing alternatives at the time; first works on sharing have focused on economic aspects
they also anticipate two crucial paradigms: (i) dynamic and market regulation policies associated to the intro-
spectrum trading and (ii) the decoupling of the network duction of MVNOs. However, the main limitation of
infrastructure from services, enabled by infrastructure these approaches was due to the mobile technology that
sharing. It is worth noticing that both these paradigms prevented a significant service and performance differen-
are ongoing research topics even nowadays. Similarly, tiation among users of MVNOs and MNOs. Therefore,
according to [16], the advantages of network sharing go sharing policies had to be based on other objectives such
beyond cost reduction: based on the product life cy- as cooperative coverage of low population areas and cost
cle model, the authors suggest that, under an appropri- sharing of radio towers.
ate regulatory framework, network sharing can steer the As mentioned above, the key aspect that we take from
monolithic mobile networks industry toward the decou- these works is the decoupling of network services from
pling of the network infrastructure from services for end the infrastructure that provides them. Only recently,
users. In other words, based on [142] and [16] infras- however, this concept has become fully exploitable
tructure sharing would lead to new stakeholders such thanks to the network virtualization technologies that
as network/infrastructure providers (InPs) and service allow a fine grain differentiation of the network behav-
providers (SPs) which were expected to emerge in the ior with respect to different applications and groups of
© International Telecommunication Union, 2020 143