Page 454 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 454
2 Cloud Computing management
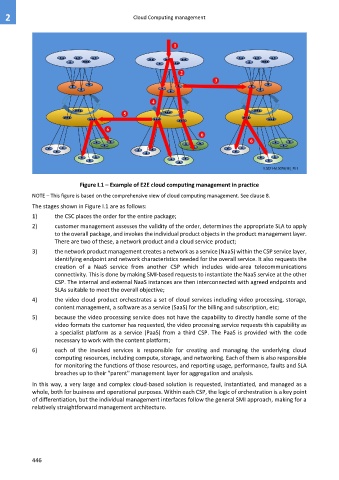
Figure I.1 – Example of E2E cloud computing management in practice
NOTE – This figure is based on the comprehensive view of cloud computing management. See clause 8.
The stages shown in Figure I.1 are as follows:
1) the CSC places the order for the entire package;
2) customer management assesses the validity of the order, determines the appropriate SLA to apply
to the overall package, and invokes the individual product objects in the product management layer.
There are two of these, a network product and a cloud service product;
3) the network product management creates a network as a service (NaaS) within the CSP service layer,
identifying endpoint and network characteristics needed for the overall service. It also requests the
creation of a NaaS service from another CSP which includes wide-area telecommunications
connectivity. This is done by making SMI-based requests to instantiate the NaaS service at the other
CSP. The internal and external NaaS instances are then interconnected with agreed endpoints and
SLAs suitable to meet the overall objective;
4) the video cloud product orchestrates a set of cloud services including video processing, storage,
content management, a software as a service (SaaS) for the billing and subscription, etc;
5) because the video processing service does not have the capability to directly handle some of the
video formats the customer has requested, the video processing service requests this capability as
a specialist platform as a service (PaaS) from a third CSP. The PaaS is provided with the code
necessary to work with the content platform;
6) each of the invoked services is responsible for creating and managing the underlying cloud
computing resources, including compute, storage, and networking. Each of them is also responsible
for monitoring the functions of those resources, and reporting usage, performance, faults and SLA
breaches up to their "parent" management layer for aggregation and analysis.
In this way, a very large and complex cloud-based solution is requested, instantiated, and managed as a
whole, both for business and operational purposes. Within each CSP, the logic of orchestration is a key point
of differentiation, but the individual management interfaces follow the general SMI approach, making for a
relatively straightforward management architecture.
446