Page 259 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 259
Framework and requirements for cloud computing 1
II.6 High mobility support on distributed cloud
Table II.6 – High mobility support on distributed cloud
Use case
Name High mobility support on distributed cloud.
Abstract This use case illustrates an example of high mobility support on distributed cloud.
A typical mobility support environment follows a method of modifying the packet routing path
while the location of the service is fixed. On the distributed cloud, the location of the service is
different from the conventional cloud and is located near the user. Accordingly, the distributed
cloud needs high mobility.
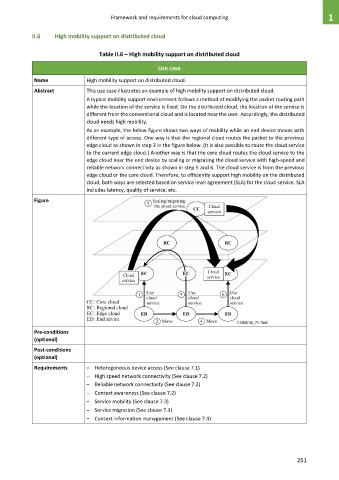
As an example, the below figure shows two ways of mobility while an end device moves with
different type of access. One way is that the regional cloud routes the packet to the previous
edge cloud as shown in step 3 in the figure below. (It is also possible to route the cloud service
to the current edge cloud.) Another way is that the core cloud routes the cloud service to the
edge cloud near the end device by scaling or migrating the cloud service with high-speed and
reliable network connectivity as shown in step 5 and 6. The cloud service is from the previous
edge cloud or the core cloud. Therefore, to efficiently support high mobility on the distributed
cloud, both ways are selected based on service level agreement (SLA) for the cloud service. SLA
includes latency, quality of service, etc.
Figure
Pre-conditions
(optional)
Post-conditions
(optional)
Requirements – Heterogeneous device access (See clause 7.1)
– High speed network connectivity (See clause 7.2)
– Reliable network connectivity (See clause 7.2)
– Context awareness (See clause 7.2)
– Service mobility (See clause 7.3)
– Service migration (See clause 7.3)
– Context information management (See clause 7.4)
251