Page 240 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 240
1 Framework and requirements for cloud computing
6 Overview of distributed cloud
6.1 Concept of distributed cloud
Cloud computing is a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical
or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand [ITU-T Y.3500]. Services in
Internet of things (IoT), augmented reality (AR)/virtual reality (VR), artificial intelligence (AI) and 5G
application domains requiring cloud infrastructure are gradually increasing and real-time services in the
above domains are also demanding especially for safety and surveillance applications.
Cloud computing has challenges to support the real-time services due to (i) the network latency between
cloud service provider (CSP) and cloud service customer (CSC), and (ii) the load congestion on the data centre.
For these challenges, what is needed is the delivery of cloud services to nearby CSCs in order to meet real-
time service delivery. Also, the distribution of cloud capabilities types to the edge of the network accessed
by CSCs are needed for load congestion.
This Recommendation introduces the distributed cloud, which is distribution of cloud capabilities types to
the edge of the network for enabling cloud service with low latency and real-time processing on limited
bandwidth by interworking among a pool of physical or virtual resources.
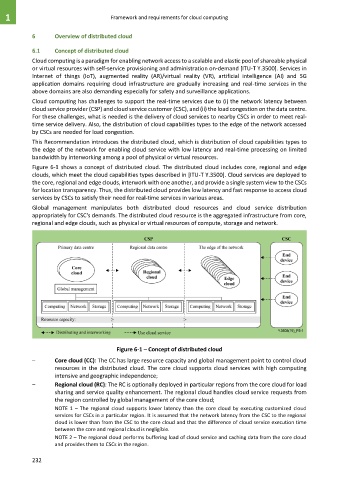
Figure 6-1 shows a concept of distributed cloud. The distributed cloud includes core, regional and edge
clouds, which meet the cloud capabilities types described in [ITU-T Y.3500]. Cloud services are deployed to
the core, regional and edge clouds, interwork with one another, and provide a single system view to the CSCs
for location transparency. Thus, the distributed cloud provides low latency and fast response to access cloud
services by CSCs to satisfy their need for real-time services in various areas.
Global management manipulates both distributed cloud resources and cloud service distribution
appropriately for CSC's demands. The distributed cloud resource is the aggregated infrastructure from core,
regional and edge clouds, such as physical or virtual resources of compute, storage and network.
Figure 6-1 – Concept of distributed cloud
– Core cloud (CC): The CC has large resource capacity and global management point to control cloud
resources in the distributed cloud. The core cloud supports cloud services with high computing
intensive and geographic independence;
– Regional cloud (RC): The RC is optionally deployed in particular regions from the core cloud for load
sharing and service quality enhancement. The regional cloud handles cloud service requests from
the region controlled by global management of the core cloud;
NOTE 1 – The regional cloud supports lower latency than the core cloud by executing customized cloud
services for CSCs in a particular region. It is assumed that the network latency from the CSC to the regional
cloud is lower than from the CSC to the core cloud and that the difference of cloud service execution time
between the core and regional cloud is negligible.
NOTE 2 – The regional cloud performs buffering load of cloud service and caching data from the core cloud
and provides them to CSCs in the region.
232