Page 123 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 123
Framework and requirements for cloud computing 1
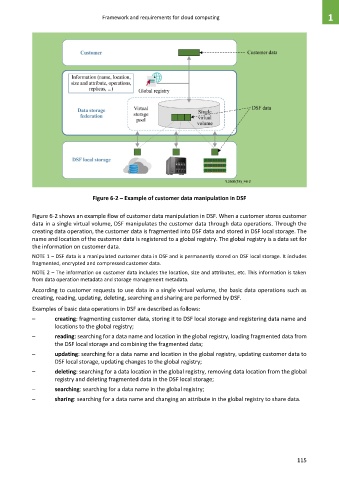
Figure 6-2 – Example of customer data manipulation in DSF
Figure 6-2 shows an example flow of customer data manipulation in DSF. When a customer stores customer
data in a single virtual volume, DSF manipulates the customer data through data operations. Through the
creating data operation, the customer data is fragmented into DSF data and stored in DSF local storage. The
name and location of the customer data is registered to a global registry. The global registry is a data set for
the information on customer data.
NOTE 1 – DSF data is a manipulated customer data in DSF and is permanently stored on DSF local storage. It includes
fragmented, encrypted and compressed customer data.
NOTE 2 – The information on customer data includes the location, size and attributes, etc. This information is taken
from data operation metadata and storage management metadata.
According to customer requests to use data in a single virtual volume, the basic data operations such as
creating, reading, updating, deleting, searching and sharing are performed by DSF.
Examples of basic data operations in DSF are described as follows:
– creating: fragmenting customer data, storing it to DSF local storage and registering data name and
locations to the global registry;
– reading: searching for a data name and location in the global registry, loading fragmented data from
the DSF local storage and combining the fragmented data;
– updating: searching for a data name and location in the global registry, updating customer data to
DSF local storage, updating changes to the global registry;
– deleting: searching for a data location in the global registry, removing data location from the global
registry and deleting fragmented data in the DSF local storage;
– searching: searching for a data name in the global registry;
– sharing: searching for a data name and changing an attribute in the global registry to share data.
115