Page 157 - ITU KALEIDOSCOPE, ATLANTA 2019
P. 157
ICT for Health: Networks, standards and innovation
different scenarios and requirements, such as various contributed to the digitization of data, and they started to be
wearable devices. applied in 1960s, when the United States began research on
HIS in military hospitals, and then Japan and some European
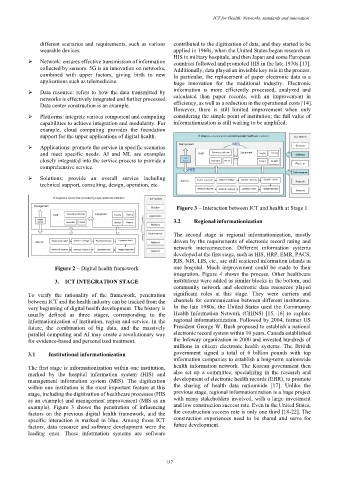
➢ Network: ensures effective transmission of information countries followed and promoted HIS in the late 1970s [13].
collected by sensors. 5G is an innovation on networks, Additionally, data played an invisible key role in the process.
combined with upper factors, giving birth to new In particular, the replacement of paper electronic data is a
applications such as telemedicine. huge innovation for the traditional industry. Electronic
➢ Data resource: refers to how the data transmitted by information is more efficiently processed, analyzed and
networks is effectively integrated and further processed. calculated than paper records, with an improvement in
Data center construction is an example. efficiency, as well as a reduction in the operational costs [14].
However, there is still limited improvement when only
➢ Platforms: integrate various component and computing considering the simple point of institution; the full value of
capabilities to achieve integration and modularity. For informationization is still waiting to be amplified.
example, cloud computing provides the foundation
support for the upper applications of digital health.
➢ Applications: promote the service in specific scenarios
and meet specific needs. AI and ML are examples
closely integrated into the service process to provide a
comprehensive service.
➢ Solutions: provide an overall service including
technical support, consulting, design, operation, etc.
Figure 3 – Interaction between ICT and health at Stage 1
3.2 Regional informationization
The second stage is regional informationization, mostly
driven by the requirements of electronic record rating and
network interconnection. Different information systems
developed at the first stage, such as HIS, HRP, EMR, PACS,
RIS, NIS, LIS, etc., are still scattered information islands in
Figure 2 – Digital health framework one hospital. Much improvement could be made to their
integration, Figure 4 shows the process. Other healthcare
3. ICT INTEGRATION STAGE institutions were added as similar blocks in the bottom, and
community network and electronic data resources played
To verify the rationality of the framework, penetration significant roles at this stage. They were carriers and
between ICT and the health industry can be tracked from the channels for communication between different institutions.
very beginning of digital health development. The history is In the late 1980s, the United States used the Community
usually defined as three stages, corresponding to the Health Information Network (CHINS) [15, 16] to explore
informationization of institution, region and service. In the regional informationization. Followed by 2004, former US
future, the combination of big data, and the massively President George W. Bush proposed to establish a national
parallel computing and AI may create a revolutionary way electronic record system within 10 years. Canada established
for evidence-based and personalized treatment. the Infoway organization in 2000 and invested hundreds of
millions in citizen electronic health systems. The British
3.1 Institutional informationization government signed a total of 6 billion pounds with top
information companies to establish a long-term nationwide
The first stage is informationization within one institution, health information network. The Korean government then
marked by the hospital information system (HIS) and also set up a committee, specializing in the research and
management information system (MIS). The digitization development of electronic health records (EHR), to promote
within one institution is the most important feature at this the sharing of health data nationwide [17]. Unlike the
stage, including the digitization of healthcare processes (HIS previous stage, regional informationization is a huge project
as an example) and management improvement (MIS as an with many stakeholders involved, with a large investment
example). Figure 3 shows the penetration of influencing and low construction success rate. Even in the United States,
factors on the previous digital health framework, and the the construction success rate is only one third [18-22]. The
specific interaction is marked in blue. Among those ICT construction experiences need to be shared and serve for
factors, data resource and software development were the future development.
leading ones. These information systems are software
– 137 –