Page 99 - Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications
P. 99
2 Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications 2
II.2.5.2 Big data interconnection federation mode
Title Big data interconnection federation mode
Description Big data interconnection is a model of big data exchange for enabling the interworking between
two or more data sources (e.g., data providers) for mutual exchange of big datasets, by which the
source big datasets are interchanged among data sources (e.g., data providers), contributed to the
intermediator (e.g., big data service provider) and distributed to data targets (e.g., big data service
customers).
Roles/Sub – Data provider (DP)
roles – DP:data supplier
– DP:data broker
– Big data service provider (BDSP)
– Big data service customer (BDC)
Figure
(optional)
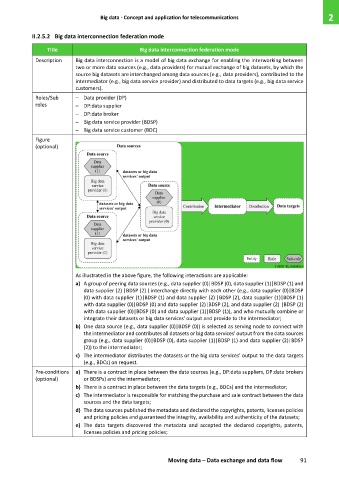
As illustrated in the above figure, the following interactions are applicable:
a) A group of peering data sources (e.g., data supplier (0)|BDSP (0), data supplier (1)|BDSP (1) and
data supplier (2) |BDSP (2) ) interchange directly with each other (e.g., data supplier (0)|BDSP
(0) with data supplier (1)|BDSP (1) and data supplier (2) |BDSP (2), data supplier (1)|BDSP (1)
with data supplier (0)|BDSP (0) and data supplier (2)|BDSP (2), and data supplier (2) |BDSP (2)
with data supplier (0)|BDSP (0) and data supplier (1)|BDSP (1)), and who mutually combine or
integrate their datasets or big data services' output and provide to the intermediator;
b) One data source (e.g., data supplier (0)|BDSP (0)) is selected as serving node to connect with
the intermediator and contributes all datasets or big data services' output from the data sources
group (e.g., data supplier (0)|BDSP (0), data supplier (1)|BDSP (1) and data supplier (2)|BDSP
(2)) to the intermediator;
c) The intermediator distributes the datasets or the big data services' output to the data targets
(e.g., BDCs) on request.
Pre-conditions a) There is a contract in place between the data sources (e.g., DP:data suppliers, DP:data brokers
(optional) or BDSPs) and the intermediator;
b) There is a contract in place between the data targets (e.g., BDCs) and the intermediator;
c) The intermediator is responsible for matching the purchase and sale contract between the data
sources and the data targets;
d) The data sources published the metadata and declared the copyrights, patents, licenses policies
and pricing policies and guaranteed the integrity, availability and authenticity of the datasets;
e) The data targets discovered the metadata and accepted the declared copyrights, patents,
licenses policies and pricing policies;
Moving data – Data exchange and data flow 91