Page 91 - Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications
P. 91
2 Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications 2
Title Big data open sharing mode
Figure
(optional)
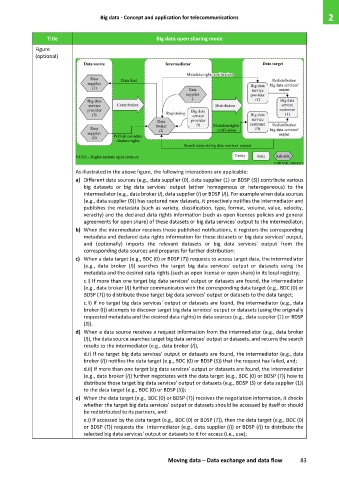
As illustrated in the above figure, the following interactions are applicable:
a) Different data sources (e.g., data supplier (0), data supplier (1) or BDSP (S)) contribute various
big datasets or big data services' output (either homogenous or heterogeneous) to the
intermediator (e.g., data broker (I), data supplier (I) or BDSP (I)). For example when data sources
(e.g., data supplier (0)) has captured new datasets, it proactively notifies the intermediator and
publishes the metadata (such as variety, classification, type, format, volume, value, velocity,
veracity) and the declared data rights information (such as open licenses policies and general
agreements for open share) of these datasets or big data services' output to the intermediator;
b) When the intermediator receives those published notifications, it registers the corresponding
metadata and declared data rights information for these datasets or big data services' output,
and (optionally) imports the relevant datasets or big data services' output from the
corresponding data sources and prepares for further distribution;
c) When a data target (e.g., BDC (0) or BDSP (T)) requests to access target data, the intermediator
(e.g., data broker (I)) searches the target big data services' output or datasets using the
metadata and the desired data rights (such as open license or open share) in its local registry;
c.i) If more than one target big data services' output or datasets are found, the intermediator
(e.g., data broker (I)) further communicates with the corresponding data target (e.g., BDC (0) or
BDSP (T)) to distribute those target big data services' output or datasets to the data target;
c.ii) If no target big data services' output or datasets are found, the intermediator (e.g., data
broker (I)) attempts to discover target big data services' output or datasets (using the originally
requested metadata and the desired data rights) in data sources (e.g., data supplier (1) or BDSP
(S)).
d) When a data source receives a request information from the intermediator (e.g., data broker
(I)), the data source searches target big data services' output or datasets, and returns the search
results to the intermediator (e.g., data broker (I)),
d.i) If no target big data services' output or datasets are found, the intermediator (e.g., data
broker (I)) notifies the data target (e.g., BDC (0) or BDSP (S)) that the request has failed, and;
d.ii) If more than one target big data services' output or datasets are found, the intermediator
(e.g., data broker (I)) further negotiates with the data target (e.g., BDC (0) or BDSP (T)) how to
distribute those target big data services' output or datasets (e.g., BDSP (S) or data supplier (1))
to the data target (e.g., BDC (0) or BDSP (S));
e) When the data target (e.g., BDC (0) or BDSP (T)) receives the negotiation information, it checks
whether the target big data services' output or datasets should be accessed by itself or should
be redistributed to its partners, and:
e.i) If accessed by the data target (e.g., BDC (0) or BDSP (T)), then the data target (e.g., BDC (0)
or BDSP (T)) requests the intermediator (e.g., data supplier (I)) or BDSP (I)) to distribute the
selected big data services' output or datasets to it for access (i.e., use);
Moving data – Data exchange and data flow 83