Page 239 - Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications
P. 239
Big data - Concept and application for telecommunications 5
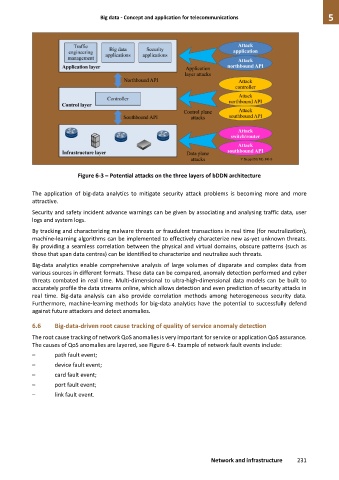
Figure 6-3 – Potential attacks on the three layers of bDDN architecture
The application of big-data analytics to mitigate security attack problems is becoming more and more
attractive.
Security and safety incident advance warnings can be given by associating and analysing traffic data, user
logs and system logs.
By tracking and characterizing malware threats or fraudulent transactions in real time (for neutralization),
machine-learning algorithms can be implemented to effectively characterize new as-yet unknown threats.
By providing a seamless correlation between the physical and virtual domains, obscure patterns (such as
those that span data centres) can be identified to characterize and neutralize such threats.
Big-data analytics enable comprehensive analysis of large volumes of disparate and complex data from
various sources in different formats. These data can be compared, anomaly detection performed and cyber
threats combated in real time. Multi-dimensional to ultra-high-dimensional data models can be built to
accurately profile the data streams online, which allows detection and even prediction of security attacks in
real time. Big-data analysis can also provide correlation methods among heterogeneous security data.
Furthermore, machine-learning methods for big-data analytics have the potential to successfully defend
against future attackers and detect anomalies.
6.6 Big-data-driven root cause tracking of quality of service anomaly detection
The root cause tracking of network QoS anomalies is very important for service or application QoS assurance.
The causes of QoS anomalies are layered, see Figure 6-4. Example of network fault events include:
– path fault event;
– device fault event;
– card fault event;
– port fault event;
– link fault event.
Network and infrastructure 231