Page 28 - U4SSC Collection Methodology for Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities
P. 28
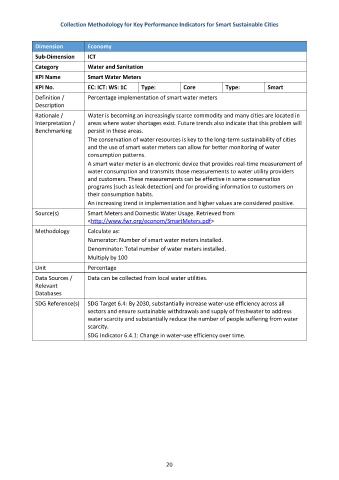
Collection Methodology for Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities
Dimension Economy
Sub-Dimension ICT
Category Water and Sanitation
KPI Name Smart Water Meters
KPI No. EC: ICT: WS: 1C Type: Core Type: Smart
Definition / Percentage implementation of smart water meters
Description
Rationale / Water is becoming an increasingly scarce commodity and many cities are located in
Interpretation / areas where water shortages exist. Future trends also indicate that this problem will
Benchmarking persist in these areas.
The conservation of water resources is key to the long-term sustainability of cities
and the use of smart water meters can allow for better monitoring of water
consumption patterns.
A smart water meter is an electronic device that provides real-time measurement of
water consumption and transmits those measurements to water utility providers
and customers. These measurements can be effective in some conservation
programs (such as leak detection) and for providing information to customers on
their consumption habits.
An increasing trend in implementation and higher values are considered positive.
Source(s) Smart Meters and Domestic Water Usage. Retrieved from
<http://www.fwr.org/econom/SmartMeters.pdf>
Methodology Calculate as:
Numerator: Number of smart water meters installed.
Denominator: Total number of water meters installed.
Multiply by 100
Unit Percentage
Data Sources / Data can be collected from local water utilities.
Relevant
Databases
SDG Reference(s) SDG Target 6.4: By 2030, substantially increase water-use efficiency across all
sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address
water scarcity and substantially reduce the number of people suffering from water
scarcity.
SDG Indicator 6.4.1: Change in water-use efficiency over time.
20