Page 106 - U4SSC Collection Methodology for Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities
P. 106
Collection Methodology for Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities
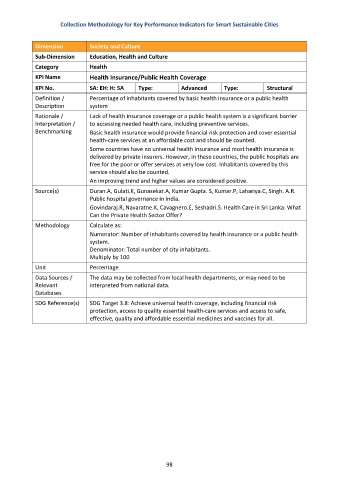
Dimension Society and Culture
Sub-Dimension Education, Health and Culture
Category Health
KPI Name Health Insurance/Public Health Coverage
KPI No. SA: EH: H: 5A Type: Advanced Type: Structural
Definition / Percentage of inhabitants covered by basic health insurance or a public health
Description system
Rationale / Lack of health insurance coverage or a public health system is a significant barrier
Interpretation / to accessing needed health care, including preventive services.
Benchmarking Basic health insurance would provide financial risk protection and cover essential
health-care services at an affordable cost and should be counted.
Some countries have no universal health insurance and most health insurance is
delivered by private insurers. However, in these countries, the public hospitals are
free for the poor or offer services at very low cost. Inhabitants covered by this
service should also be counted.
An improving trend and higher values are considered positive.
Source(s) Duran.A, Gulati.K, Gunasekar.A, Kumar Gupta. S, Kumar.P, Lahariya.C, Singh. A.R.
Public hospital governance in India.
Govindaraj.R, Navaratne.K, Cavagnero.E, Seshadri.S. Health Care in Sri Lanka: What
Can the Private Health Sector Offer?
Methodology Calculate as:
Numerator: Number of inhabitants covered by health insurance or a public health
system.
Denominator: Total number of city inhabitants.
Multiply by 100
Unit Percentage
Data Sources / The data may be collected from local health departments, or may need to be
Relevant interpreted from national data.
Databases
SDG Reference(s) SDG Target 3.8: Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk
protection, access to quality essential health-care services and access to safe,
effective, quality and affordable essential medicines and vaccines for all.
98