Page 86 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 86
1 Trust in ICT
blockchain technology to the environment of IoT provides trustful potentials. Since the time an invention
finishes final assembly, the M2M services provider into a universal blockchain representing its starting of life
could register it. In addition, when sold a trader or end buyer could register it to a local blockchain public or
private area. When registered, the device stays a unique entity within the blockchain during its life [106].
Consequently, in a blockchain relied on IoT, the ability of preserving product data, its history, product
revisions, guarantee details and end of life in the blockchain becomes the Blockchain itself can mean the
trusted product database. Therefore, we can use this technology in various IoT use cases as real example
requirements to enhance trust among heterogeneous sensors with complicated service relationships.
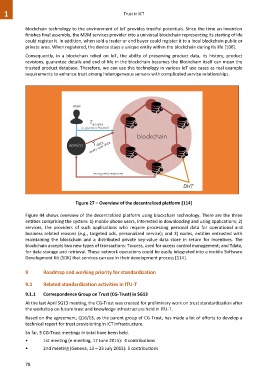
Figure 27 – Overview of the decentralized platform [114]
Figure 44 shows overview of the decentralized platform using blockchain technology. There are the three
entities comprising the system: 1) mobile phone users, interested in downloading and using applications; 2)
services, the providers of such applications who require processing personal data for operational and
business related reasons (e.g., targeted ads, personalized service); and 3) nodes, entities entrusted with
maintaining the blockchain and a distributed private key-value data store in return for incentives. The
blockchain accepts two new types of transactions: Taccess, used for access control management; and Tdata,
for data storage and retrieval. These network operations could be easily integrated into a mobile Software
Development Kit (SDK) that services can use in their development process [114].
9 Roadmap and working priority for standardization
9.1 Related standardization activities in ITU-T
9.1.1 Correspondence Group on Trust (CG-Trust) in SG13
At the last April SG13 meeting, the CG-Trust was created for preliminary work on trust standardization after
the workshop on future trust and knowledge infrastructure held in ITU-T.
Based on the agreement, Q16/13, as the parent group of CG-Trust, has made a lot of efforts to develop a
technical report for trust provisioning in ICT infrastructure.
So far, 5 CG-Trust meetings in total have been held.
• 1st meeting (e-meeting, 17 June 2015): 4 contributions
• 2nd meeting (Geneva, 13 – 23 July 2015): 5 contributions
78