Page 5 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 5
First new ITU standards on trust
Based on the significant efforts made to build converged Information and Communications Technology (ICT)
services and a reliable information infrastructure while taking into account social and economic
considerations, ITU members have focused on trust standardization. For this, ITU newly defined that ‘trust’
is the measureable belief and/or confidence which represents accumulated value from history and the
expecting value for future. ITU also recognized that, in ICT environments, trust affects the preference of an
entity to consume a particular service offered by another entity and it affects the decision making of an entity
to transact with another entity. Furthermore, trust is a broader concept that can cover security and privacy
as trust revolves confidence that people, data and devices will function or behave in expected ways as well
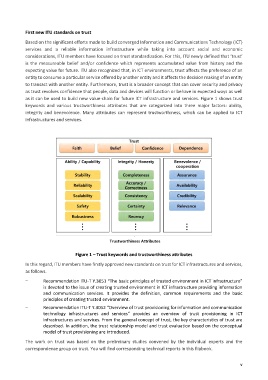
as it can be used to build new value-chain for future ICT infrastructure and services. Figure 1 shows trust
keywords and various trustworthiness attributes that are categorized into three major factors: ability,
integrity and benevolence. Many attributes can represent trustworthiness, which can be applied to ICT
infrastructures and services.
Figure 1 – Trust keywords and trustworthiness attributes
In this regard, ITU members have firstly approved new standards on trust for ICT infrastructures and services,
as follows.
– Recommendation ITU-T Y.3051 “The basic principles of trusted environment in ICT infrastructure”
is devoted to the issue of creating trusted environment in ICT infrastructure providing information
and communication services. It provides the definition, common requirements and the basic
principles of creating trusted environment.
– Recommendation ITU-T Y.3052 “Overview of trust provisioning for information and communication
technology infrastructures and services” provides an overview of trust provisioning in ICT
infrastructures and services. From the general concept of trust, the key characteristics of trust are
described. In addition, the trust relationship model and trust evaluation based on the conceptual
model of trust provisioning are introduced.
The work on trust was based on the preliminary studies convened by the individual experts and the
correspondence group on trust. You will find corresponding technical reports in this flipbook.
v