Page 174 - Proceedings of the 2017 ITU Kaleidoscope
P. 174
2017 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
chain based edge caching scheme to minimize the transmis-
Table 1. Parameter Definition
sion cost of base stations, whereby the traffic offloading is
Name Description
taken into consideration.
The interest packet transmission delay
int
d
MC from the user to the MBS
3. SYSTEM MODEL
The interest packet transmission delay
int
d MC,1
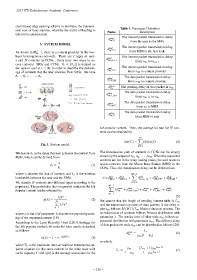
As shown in Fig. 1, there is a content provider in the two- from MBS to the first node
layer heterogeneous network. There are I types of user- int The interest packet transmission delay
s and N contents in CCNs. Users have two ways to ac- d m,m+1
from n m to n m+1
cess contents: SBSs and CCNs. θ i ∈ [0, 1] is defined as
the type of user i( i ∈ I), in order to describe the percent- d int The interest packet transmission delay
M,CP
age of contents that the user achieves from SBSs. We have from n M to content provider
θ 1 < θ i < · · · < θ I . The data packet transmission delay
d dat
CP,M from n M to content provider
d wai
m The pending delay of data packet in n m
The data packet transmission delay
dat
d m+1,m
from n m+1 to n m
The data packet transmission delay
dat
d 1,MC
from n 1 to MBS
The data packet transmission delay
d dat
MC
from MBS to user
kth popular content. Then, the average hit rate for N con-
tents can be obtained by
N
X
hit(C) = p(k)h(k) (4)
Fig. 1. System model.
k=1
The transmission path of contents in CCNs can be simply
We denote d 1 as the delay that user achieves the content from
shown by the sequence n 1 , n 2 , · · · , n M . When the requested
SBSs, which can be derived from
contents are not in the relay routing nodes, the user needs to
u
d 1 = (1) access contents from the Macro-Base Station (MBS) in the
b 1 CCNs. Thus, the transmission delay can be derived from
where u denotes the size of content, and b 1 is the wireless M−1
X int int dat
int
int
bandwidth between the user and the SBSs. d =d MC + d MC,1 + d m,m+1 + d M,CP + d CP,M +
We classify N contents into different types according to the m=1
popularity. The probability that a requested content is the kth M−1 wai dat wai dat dat
X
popular content can be obtained by (d m + d m+1,m ) + d M + d 1,MC + d MC
m=1
1/k α (5)
p(k) = (2)
We assume that the length of pending interest table is L m
N P
1/γ α and the transmission process of data packets in the relay n-
γ=1
ode n m follows M/M/1/L m Markov decision process. The
where α is the Zipf parameter. k denotes the popularity rank- arrival process of contents follows Poisson distribution with
ing of the requested content [19]. parameter λ. The service time of relay node n m follows ex-
ponential distribution with parameter µ m . The delivery delay
According to the Least Recently Used (LRU) strategy, for
of data packets in node n m can be described as follows [20]:
the kth popular content, its cache hit ratio can be described
as follows wai L s
d m = (6)
µ m (1 − π 0 )
h(k) = 1 − e −q(k)T C (3)
in which,
where T C is the maximum inter-arrival time between two ad-
L m +1
jacent requests for the same content in the relay node with L s = ρ m − (L m + 1)ρ m (7)
cache capacity C and q(k) is the average access rate for the 1 − ρ m 1 − ρ m L m +1
– 158 –