Page 179 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 179
ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables 3
By application of MEC and SFC in mobile network, operator can extend the network softwarization scope into
service application domain, to support programmability on applications platform at edge network.
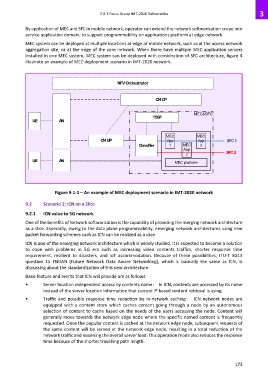
MEC system can be deployed at multiple locations at edge of mobile network, such as at the access network
aggregation site, or at the edge of the core network. When there have multiple MEC application servers
installed in one MEC system, MEC system can be deployed with combination of SFC architecture, figure 4
illustrate an example of MEC deployment scenario in IMT-2020 network.
NFV Orchestrator
CN CP
MEC&SFC
TSSF
UE AN
MEC MEC
CN UP App App SFC 1
Classifier 1 MEC 3
App
2 SFC 2
UE AN MEC platform
Figure 9.1-1 – An example of MEC deployment scenario in IMT-2020 network
9.2 Scenario 2: ICN on a Slice
9.2.1 ICN value to 5G network
One of the benefits of Network softwarization is the capability of providing the merging network architecture
as a slice. Especially, owing to the data plane programmability, emerging network architectures using new
packet forwarding schemes such as ICN can be realized as a slice.
ICN is one of the emerging network architecture which is widely studied. It is expected to become a solution
to cope with problems in 5G era such as increasing video contents traffics, shorter response time
requirement, resilient to disasters, and IoT accommodation. Because of these possibilities, ITU-T SG13
question 15 FNDAN (Future Network Data Aware Networking), which is basically the same as ICN, is
discussing about the standardization of this new architecture.
Basic feature and merits that ICN will provide are as follows:
• Server location independent access by contents name: In ICN, contents are accessed by its name
instead of the server location information that current IP based content retrieval is using.
• Traffic and possible response time reduction by in-network caching: ICN network nodes are
equipped with a content store which caches content going through a node by an autonomous
selection of content to cache based on the needs of the users accessing the node. Content will
generally move towards the network edge node where the specific named content is frequently
requested. Once the popular content is cached at the network edge node, subsequent requests of
the same content will be served at the network edge node, resulting in a total reduction of the
network traffic and lessening the overall server load. This operation mode also reduces the response
time because of the shorter travelling path length.
173