Page 854 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 854
2 Transport aspects
11.2.2.19 Non-standard facility commands and responses
The non-standard facility (NSF) commands may be used to exchange vendor-discretionary information
between the FTUs. The NSF Request command is shown in Table 11-53 and may be initiated by either FTU
to request the non-standard information. The responses shall be as shown in Table 11-54. The first byte of
either the command or a response shall be the assigned value for the NSF command type, as shown in
Table 11-5 for normal priority NSF commands, or in Table 11-6 for low priority NSF commands. The
remaining bytes of normal priority and low priority commands shall be as shown in Table 11-53. The second
byte of normal priority and low priority responses shall be as shown in Table 11-54. The bytes shall be sent
using the format described in clause 11.2.2.1.
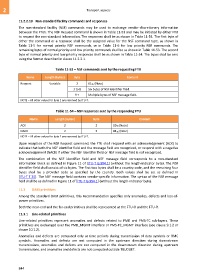
Table 11-53 – NSF commands sent by the requesting FTU
Name Length (bytes) Byte Content
Request Variable 2 0116 (Note)
3 to 8 Six bytes of NSF identifier field.
9 + Multiple bytes of NSF message field.
NOTE – All other values for byte 2 are reserved by ITU-T.
Table 11-54 – NSF responses sent by the responding FTU
Name Length (bytes) Byte Content
ACK 2 2 8016 (Note)
NACK 2 2 8116 (Note)
NOTE – All other values for byte 2 are reserved by ITU-T.
Upon reception of the NSF Request command, the FTU shall respond with an acknowledgement (ACK) to
indicate that both the NSF identifier field and the message field are recognized, or respond with a negative
acknowledgement (NACK) if either the NSF identifier field or NSF message field is not recognized.
The combination of the NSF identifier field and NSF message field corresponds to a non-standard
information block as defined in Figure 11 of [ITU-T G.994.1] (without the length-indicator byte). The NSF
identifier field shall consist of six bytes. The first two bytes shall be a country code, and the remaining four
bytes shall be a provider code as specified by the country. Both values shall be set as defined in
[ITU-T T.35]. The NSF message field contains vendor-specific information. The syntax of the NSF message
field shall be as defined in Figure 11 of [ITU-T G.994.1] (without the length-indicator byte).
11.3 OAM primitives
Among the standard OAM primitives, this Recommendation specifies only anomalies, defects and loss-of-
power primitives.
Both the near-end and the far-end primitives shall be represented at the FTU-O and the FTU-R.
11.3.1 Line-related primitives
Line-related primitives represent anomalies and defects related to PMD and PMS-TC sub-layers. These
primitives are exchanged over the PMD_MGMT interface or PMS-TC_MGMT interface (see clause 9.1.2 or
clause 10.1.2).
Anomalies and defects are computed only at time periods during transmission of data symbols or RMC
symbols. Anomalies and defects are not computed in the upstream direction during downstream
transmissions, anomalies and defects are not computed in the downstream direction during upstream
transmissions, and anomalies and defects are not computed outside TBUDGET.
844