Page 833 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 833
Transport aspects 2
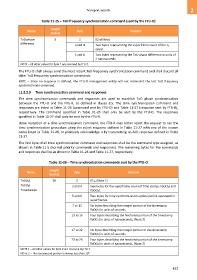
Table 11-25 – ToD frequency synchronization command (sent by the FTU-O)
Length
Name Byte Content
(bytes)
ToD phase 5 2 0216 (Note)
difference
3 and 4 Two bytes representing the superframe count of the t1
event.
5 and 6 Two bytes representing the ToD phase difference in units of
2 nanoseconds.
NOTE – All other values for byte 2 are reserved by ITU-T.
The FTU-O shall always send the most recent ToD frequency synchronization command and shall discard all
older ToD frequency synchronization commands.
NOTE – Since no response is defined, the FTU-O management entity will not retransmit the lost ToD frequency
synchronization command.
11.2.2.9 Time synchronization command and responses
The time synchronization commands and responses are used to establish ToD phase synchronization
between the FTU-O and the FTU-R, as defined in clause 8.5. The time synchronization command and
responses are listed in Table 11-26 (command sent by FTU-O) and Table 11-27 (response sent by FTU-R),
respectively. The command specified in Table 11-26 shall only be sent by the FTU-O. The responses
specified in Table 11-27 shall only be sent by the FTU-R.
Upon reception of a time synchronization command, the FTU-R may either reject the request to run the
time synchronization procedure using the reject response defined in Table 11-27 with one of the reason
codes listed in Table 11-28, or positively acknowledge it by transmitting an ACK response defined in Table
11-27.
The first byte of all time synchronization command and responses shall be the command type assigned, as
shown in Table 11-5 (normal priority commands and responses). The remaining bytes for the commands
and responses shall be as shown in Table 11-26 and Table 11-27, respectively.
Table 11-26 – Time synchronization commands sent by the FTU-O
Length
Name Byte Content
(bytes)
ToD(t1) 26 2 0116 (Note 1)
ToD(t4) 3 and 4 Two bytes for the superframe count of time stamps ToD(t1) and
Timestamps ToD(t4).
5 and 6 Two bytes for time synchronization update period expressed in
superframes.
7 to 12 Six bytes describing the integer portion of the timestamp
ToD(t1) in units of seconds.
13 to 16 Four bytes describing the fractional portion of the timestamp
ToD(t1) in units of nanoseconds. (Note 2)
17 to 22 Six bytes describing the integer portion of the timestamp
ToD(t4) in units of seconds.
23 to 26 Four bytes describing the fractional portion of the timestamp
ToD(t4) in units of nanoseconds. (Note 2)
NOTE 1 – All other values for byte 2 are reserved by ITU-T.
9
NOTE 2 – The nanosecond portion is always less than 10 .
823