Page 575 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 575
Applications 1
technically, since the location decisions may have dynamic results over time. Therefore, in the process of
developing improved product flow control in the local product supply chain, it can prove essential to try
detailed location analysis to map and cluster producers, to determine the optimum location of gathering and
distribution centres, to analyse routes to optimize them for product gathering and distribution, and to
simulate route distance and delivery time.
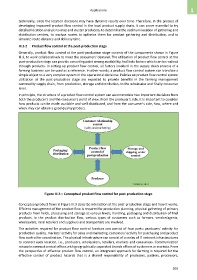
III.3.2 Product flow control at the post-production stage
Generally, product flow control at the post-production stage consists of the components shown in Figure
III.3, to work collaboratively to meet the consumers' demand. The utilization of product flow control at the
post-production stage can provide a meeting point among availability, facilitate factors which can be realized
through products. In setting up product flow control, all factors involved in the supply chain process of a
farming business can be used as a reference. In other words, a product flow control system can translate a
simple object to a very complex system in the operational decisions. Policies on product flow control system
utilization at the post-production stage are expected to provide benefits in the farming management
commodity supply chain, from production, storage and distribution, to the wholesaler and finally consumer
level.
In principle, the structure of a product flow control system can accommodate two important decisions from
both the producer's and the consumer's point of view. From the producer's side, it is important to consider
how products can be made available and well distributed, and from the consumer's side, how, where and
when they can obtain a good quality product.
Figure III.3 – Conceptual product flow control for post-production stage
Conceptual product flows in Figure III.3 describe interaction at the post-production stage and how it works.
Efficient management of the product flow is required for production planning, physical gathering of primary
products from fields, processing and storage at various levels, handling, packaging and distribution of final
products. In the product distribution flow, various types of customers such as farmers, vendor/agents,
wholesalers, rural retailers and suppliers and transporters are involved.
The activities required for product flow control function can consist of four parts: producers' activity for
production quality, markets' activity for sales and marketing, customers' activity for purchasing and product
flow control for coordination. The physical infrastructure can consist of a series of IT network infrastructures
to connect each location, i.e., producers, wholesalers, retailers, markets and consumers. Communication
networks connect central offices with geographically separated branch offices of customers or markets. From
the perspective of effective product flow control, an integrated approach for farming is required for the
effective control of product hazards that is a shared responsibility of producers, packers, processors,
565