Page 539 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 539
Core network aspects 1
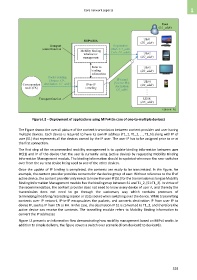
Figure I.2 – Deployment of applications using MIPv4 (in case of one-to-multiple devices)
The Figure shows the overall picture of the content transmission between content provider and user having
multiple devices. Each device is required to have its own IP address (T1_1, T1_2, …, T1_N) along with IP of
user (S1) that represents all the devices owned by the IP user. The user IP has to be assigned prior to or at
the first connection.
The first step of the recommended mobility management is to update binding information between user
IP(S1) and IP of the device that the user is currently using (active device) by requesting Mobility Binding
Information Management module. The binding information should be updated whenever the user switches
over from the current device being used to one of the other devices.
Once the update of IP binding is completed, the contents are ready to be transmitted. In the figure, for
example, the content provider provides contents for the device group of user. Without reference to the IP of
active device, the content provider only needs to know the user IP (S1) for the transmission as long as Mobility
Binding Information Management module has the binding map between S1 and T1_2, [S1:T1_2]. In virtue of
the recommendation, the content provider does not need to know every device of user A, and thereby the
transmission does not need to go through the customary way which contains processes of
terminating/modifying/recreating session or data socket when switching over the device. While transmitting
contents over IP network, IP-in-IP encapsulates the packets, and converts destination IP from user IP to
device IP, source IP from CN to HA. In this case, the destination IP S1 is converted to T1_2, and therefore the
active device can receive the contents. The tunnelling module refers to Mobility Binding information to
convert the IP addresses
Figure I.3 presents an information flow demonstrating how mobility management based on MIPv4 works. In
addition to simple delivery, the figure covers a switch over scenario (from device#2 to device#3).
529