Page 478 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 478
1 Core network aspects
NACF MMCF RACF
HGWC-FE
MLM-FE PD-FE
TUP-FE TLM-FE
TAA-FE NAC-FE
HCF TRC-FE
AM-FE
UE Control plane
Forwarding plane
AR-FE
AN-FE EN-FE ABG-FE IBG-FE
L2 transport L3 transport Packet transport
functions functions functions
Access transport Core transport
Y.2018(09)_F01
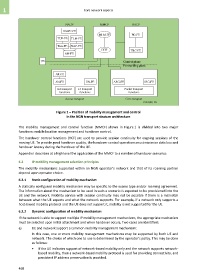
Figure 1 – Position of mobility management and control
in the NGN transport stratum architecture
The mobility management and control function (MMCF) shown in Figure 1 is divided into two major
functions: mobile location management and handover control.
The handover control functions (HCF) are used to provide session continuity for ongoing sessions of the
moving UE. To provide good handover quality, the handover control operations must minimize data loss and
handover latency during the handover of the UE.
Appendix I describes at a high level the application of the MMCF to a number of handover scenarios.
6.2 IP mobility management selection principles
The mobility mechanisms supported within an NGN operator's network and that of its roaming partner
depend upon operator choice.
6.2.1 Static configuration of mobility mechanism
A statically configured mobility mechanism may be specific to the access type and/or roaming agreement.
The information about the mechanism to be used in such a scenario is expected to be provisioned into the
UE and the network. Mobility service with session continuity may not be possible if there is a mismatch
between what the UE expects and what the network supports. For example, if a network only supports a
host-based mobility protocol and the UE does not support it, mobility is not supported for the UE.
6.2.2 Dynamic configuration of mobility mechanism
If the network is able to support multiple IP mobility management mechanisms, the appropriate mechanism
must be selected upon initial attachment and when handover occurs. Two cases are identified:
a) UE and network support a common mobility management mechanism:
In this case, one or more mobility management mechanisms may be supported by both UE and
network. The choice of which one to use is determined by the operator's policy. This may be done
as follows:
• If the UE indicates support of network-based mobility only and the network supports network-
based mobility, then a network-based mobility protocol is used for providing connectivity, and
persistent IP address preservation is provided.
468