Page 335 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 335
Core network aspects 1
The keywords "is not recommended" indicate a requirement which is not recommended but which is not
specifically prohibited. Thus, conformance with this Recommendation can still be claimed even if this
requirement is present.
The keywords "can optionally" indicate an optional requirement which is permissible, without implying any
sense of being recommended. This term is not intended to imply that the vendor's implementation must
provide the option and the feature can be optionally enabled by the network operator/service provider.
Rather, it means the vendor may optionally provide the feature and still claim conformance with this
Recommendation.
6 Multi-connection requirements
The multi-connection capability facilitates realization of the use cases described in [b-ITU-T Y-Sup.9], such as
balancing network load, higher throughput via connection aggregation or service transfer across connections.
Take video conferencing as an example, the voice may be carried by a 2G or 3G network to assure real-time
service via a circuit switch network, while the video component may be transmitted via the wireless local
area network (WLAN).
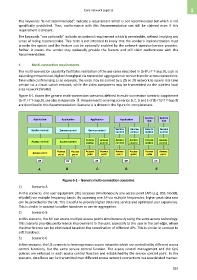
Figure 6-1 shows the generic multi-connection scenarios defined in multi-connection scenario supplement
[b-ITU-T Y-Sup.9], see also in Appendix Ⅱ. Requirements covering scenarios B, C, D and E of [b-ITU-T Y-Sup.9]
are described in this Recommendation. Scenario A is shown in the figure for completeness.
Applica Applica
Application Application Application Application
tion tion
Service Service Service Service
Service control Service control Service control
control control control control
Access Access Access Access Access Access
Access control Access control control control control control control control
Access Access Access Access Access Access Access Access
Access point
point point point point point point point point
UE UE UE UE UE
A B C D E
Figure 6-1 – Generic multi-connection scenarios
1) Scenario A
In this scenario, one user equipment (UE) accesses simultaneously one access point (AP) (e.g. BSS, NodeB,
eNodeB) via multiple frequency bands. By accessing one AP via multiple frequencies, higher peak data rate
can be provided to the UE. This is useful to provide higher data rate service and optimized user experience.
This is similar in concept to softer handover or carrier aggregation.
2) Scenario B
In this scenario, the UE can access multiple access points simultaneously using the same access technology.
This scenario provides performance improvement to the user, especially to the user in the cell edge, where
the interference can be eliminated based on the coordination of different APs. This is similar in concept to
soft handover.
3) Scenario C
In this scenario, the UE connects to heterogeneous access networks which are controlled by different access
control functions, but the same service control function. The access control management and the QoS
policies are enforced in each access control function and established by the service control point. In this
scenario, data flows can be transmitted over different access network connections in a coordinated manner.
325