Page 286 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 286
1 Core network aspects
7 Solutions
7.1 Overview
According to the requirements in clause 6.2, there are several solutions. Some solutions would help the
network to discover its neighbours, while others would enhance the terminal's capability to do so. The access-
select policy can also be made by either the network or the terminal.
7.2 Access discovery solution
7.2.1 Network-based access discovery solution
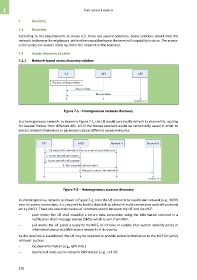
Figure 7-1 – Homogeneous accesses discovery
In a homogeneous network, as shown in Figure 7-1, the UE would continually refresh its channel list, waiting
for beacon frames from different APs. All of the frames received would be temporarily saved in order to
extract related information or parameters about different access networks.
Figure 7-2 – Heterogeneous accesses discovery
In a heterogeneous network as shown in Figure 7-2, once the UE connects to a particular network (e.g., 3GPP)
over its access connection, it is required to build a data link to a kind of multi-connection control functional
entity (MCF). There are two main modes of communications between the UE and the MCF:
– push mode: the UE shall establish a secure data connection using the information received in a
notification short message service (SMS), which is sent from MCF;
– pull mode: the UE sends a query to the MCF, to retrieve or update inter-system mobility policy or
information about available access networks in its vicinity.
As the data link is established, the UE may be required to provide related information to the MCF for policy
retrieval, such as:
– location information (e.g., GPS info.)
– discovered radio access network information (e.g., cell ID).
276