Page 241 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 241
Core network aspects 1
Preconditions
There are two MVNOs in an operator's network. MVNO-A focuses more on video services and requires all of
its video flows to go through a server for video optimization and transcoding. MVNO-B focuses more on web
service and requires these data flows to go through the servers for HTTP acceleration.
Operational flows
1) The data flows are identified and labelled before routing to the packet processing area at the (S)Gi-
LAN position based on the MVNO's identification information. The MVNO's identification
information should have higher priority than the service information when distinguishing the data
flows.
2) The flows from different MVNOs are routed to different service function entities, i.e., the flow of
MVNO-A goes through the video optimization and transcoding server, and the flow of MVNO-B goes
through the HTTP acceleration server.
I.2 Virtualization of network functions
Scenario 1: fast deployment
Descriptions
Utilizing NFV technology, fast deployment of the mobile network function uses the deployment template
which usually contains configuration and instantiation operations and parameters to realise an automatic
and dynamical deployment instead of complex manual operations.
Preconditions
The system supporting NFV is ready, and the management system can maintain and access virtual machine
(VM) images and deployment templates.
Operational flows
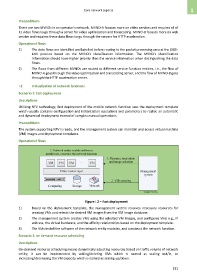
Figure I.2 – Fast deployment
1) Based on the deployment template, the management system reserves necessary resources for
creating VMs and selects the desired VM images from the VM image database.
2) The management system creates VMs using the selected VM images, and configures VMs e.g., IP
address, the virtual hardware, and the affinity relationships based on the deployment template.
3) The VMs install the software of the network entity modules, and construct the network function.
Scenario 2: on demand resource scheduling
Descriptions
On-demand resource scheduling means dynamically adjusting resources based on traffic volume of network
entity; it can be implemented by adding/deleting VMs which is named as scaling out/in, or
increasing/decreasing the VM capacity which is named as scaling up/down.
231