Page 541 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 541
Formulation and
understanding of the Setting of the context and goal
problem
Identify new and innovative SMW tools
Identification of
appropriate ICT tools
From steps 1‐2, head pilot study for e.g. 1 municipality
Incorporation of business models and market projections
Monitoring and Review steps 1‐4
evaluation
Lessons learned
Network analysis and project preparation
Delivery of solutions
Development of financing strategies and investment
Setting logical timelines
Set monitor and review process
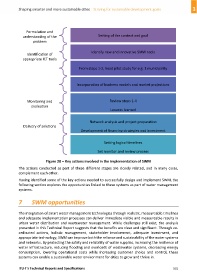
Figure 20 – Key actions involved in the implementation of SWM
The actions conducted as part of these different stages are closely related, and in many cases,
complement each other.
Having identified some of the key actions needed to successfully design and implement SWM, the
following section explores the opportunities linked to these systems as part of water management
systems.
7 SWM opportunities
The integration of smart water management technologies through realistic, measureable timelines
and adequate implementation processes can deliver immediate visible and measureable results in
urban water distribution and wastewater management. While challenges still exist, the analysis
presented in this Technical Report suggests that the benefits are clear and significant. Through co‐
ordinated actions, holistic management, stakeholder involvement, adequate investment, and
appropriate technology, SWM can improve both the reliance and sustainability of the water systems
and networks. By protecting the safety and reliability of water supplies, increasing the resilience of
water infrastructure, reducing flooding and overloads of wastewater systems, decreasing energy
consumption, lowering operational costs while increasing customer choice and control, these
systems can enable a sustainable water environment for cities to grow and thrive in.
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 531