Page 402 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 402
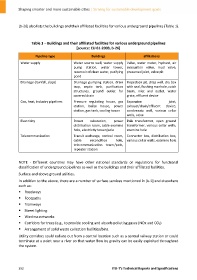
[b‐26] also lists the buildings and their affiliated facilities for various underground pipelines (Table 1).
Table 1 – Buildings and their affiliated facilities for various underground pipelines
[source: CJJ 61‐2003, b‐26]
Pipeline type Buildings affiliations
Water supply Water source well, water supply Valve, water meter, hydrant, air
pump station, water tower, evacuation valve, mud valve,
reservoir of clean water, purifying preserved joint, valve pit
pond
Drainage (rainfall, slops) Drainage pumping station, drain Inspection pit, drop well, dry box
trap, septic tank, purification with seal, flushing manhole, catch
structures, ground outlet for basin, inlet and outlet, water
covered drain grate, effluent device
Gas, heat, industry pipelines Pressure regulating house, gas Expansion joint,
station, boiler house, power exhaust/drain/effluent device,
station, gas tank, cooling tower condensate well, various cellar
wells, valve
Electricity Power substation, power Pole transformer, open ground
distribution room, cable examine transformer, various cellar wells,
hole, electricity tower/pole examine hole
Telecommunication Transit exchange, control room, Connector box, distribution box,
cable recondition hole, various cellar wells, examine hole
telecommunication tower/pole,
repeater station
NOTE ‐ Different countries may have other national standards or regulations for functional
classification of underground pipelines as well as the buildings and their affiliated facilities.
Surface and above ground utilities.
In addition to the above, there are a number of surface services mentioned in [b‐1] and elsewhere
such as:
Roadways
Footpaths
Tramways
Street lighting
Wireless networks
Corridors for trees (e.g., to provide cooling and absorb polluting gases (NOx and CO2)
Arrangement of solid waste collection facilities/bins.
Utility corridors could radiate out from a central location such as a central railway station or could
terminate at a point near a river so that water flow by gravity can be easily exploited throughout
the system.
392 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications