Page 336 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 336
Therefore, any strategy of planning for the ICT infrastructure deployment should take into account
aspects such as combating the digital divide within cities.
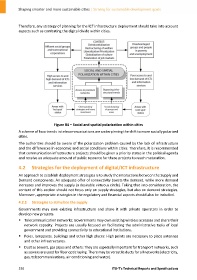
Figure 84 – Social and spatial polarization within cities
A scheme of how trends in telecommunications are underpinning the shift to more socially polarized
cities.
The authorities should be aware of the polarization problem caused by the lack of infrastructure
and the differences in economic and social conditions within cities. Therefore, it is recommended
that communication infrastructure projects should be given a priority status in the political agenda
and receive an adequate amount of public resource for these projects to reach maturation.
4.2 Strategies for the deployment of digital/ICT infrastructure
An approach to establish deployment strategies is to study the interactions between the Supply and
Demand components. An adequate offer of connectivity boosts the demand, while more demand
increases and improves the supply (a desirable virtuous circle). Taking that into consideration, the
content of this section should not focus only on supply strategies, but also on demand strategies.
Moreover, appropriate strategies in the regulatory and financial aspects should also be included.
4.2.1 Strategies to stimulate the supply
Governments may own existing infrastructure and share it with private operators in order to
develop new projects.
Telecommunication networks: Governments may own existing wireless accesses and share their
network capacity. Projects are usually focused on facilitating the administrative tasks of local
government and providing connectivity to educational institutions.
Poles, lampposts, buildings and other high places: High points are necessary to place antennas
and other infrastructures.
Duct as sewers, gas pipes and others: They are especially important for transport networks, such
as sewers are used for fiber optic laying. There may be versatile ducts for all networks (electricity,
gas, telecommunications, air conditioning and water).
326 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications