Page 29 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 29
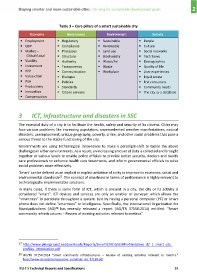
Table 3 – Core pillars of a smart sustainable city
Economy Governance Environment Society
Employment Regulatory Sustainable People
GDP Compliance Renewable Culture
Market – Processes Land use Social networks
Global/Local Structure Biodiversity Tech Savvy
Viability Authority Water/Air Demographics
Investment Transparency Waste Quality of life
PPP Communication Workplace User experiences
Value chain Dialogue Equal access
Risk Policies End consumers
Productivity Standards Community needs
Innovation Citizen services The city as a database
Compensation
3 ICT, infrastructure and disasters in SSC
The essential duty of a city is to facilitate the health, safety and security of its citizens. Cities may
face various problems like increasing population, unprecedented weather manifestations, natural
disasters, unemployment, unique geography, poverty, crime, and other social problems that pose a
serious threat to the stable functioning of the city.
Governments are using technological innovations to make a paradigm‐shift to tackle the above
challenges in urban environments. As a result, an increasing amount of data is collected and brought
together at various levels to enable police officials to provide better security, doctors and health
care professionals to enhance health care treatments, and inform governmental officials to solve
social problems more effectively.
'Smart' can be defined as an implicit or explicit ambition of a city to improve its economic, social and
27
environmental standards . The concept of smartness in terms of performance is highly relevant to
technologically implementable solutions.
In many cases, if there is some form of ICT, which is present in a city, the city or its activity is
considered "smart". ICT devices and services are only an enabler or purveyor which allows the
“smartness” to percolate throughout a system. Just by having a personal computer (PC) or smart
phone does not define "smartness" or intelligence. Specifically, the International Organization for
Standardizations (ISO) 28 has recently released a report (ISO/TR 37150:2014) entitled: “Smart
community infrastructures – Review of existing activities relevant to metrics”.
____________________
27 http://www.pleecproject.eu/downloads/Reports/Smart%20City%20Profiles/pleec_d2_1_smart_city_
profiles_introduction.pdf
28 ISO/TR 37150:2014 "Smart community infrastructures – Review of existing activities relevant to metrics."
http://www.iso.org/iso/executive_summary_iso_37150.pdf
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 19