Page 690 - Unleashing the potenti al of the Internet of Things
P. 690
5 Unleashing the potential of the Internet of Things
Appendix I
EHM service deployment technical scenarios
(This appendix does not form an integral part of this Recommendation.)
This appendix gives examples of EHM service deployment technical scenarios involving EHM
components.
I.1 Technical scenario for community EHM services
In community environment, EHM services are provided by qualified facilities and serve all
inhabitants of a community. Figure I.1 shows a deployment case for community EHM service.
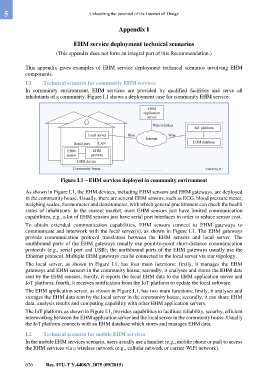
Figure I.1 – EHM services deployed in community environment
As shown in Figure I.1, the EHM devices, including EHM sensors and EHM gateways, are deployed
in the community house. Usually, there are several EHM sensors, such as ECG, blood pressure meter,
weighing scales, thermometer and densitometer, with which general practitioners can check the health
states of inhabitants. In the current market, most EHM sensors just have limited communication
capabilities, e.g., a lot of EHM sensors just have serial port interfaces in order to reduce sensor cost.
To obtain extended communication capabilities, EHM sensors connect to EHM gateways to
communicate and interwork with the local server(s), as shown in Figure I.1. The EHM gateways
provide communication protocol translation between the EHM sensors and local server. The
southbound ports of the EHM gateways usually use point-to-point short-distance communication
protocols (e.g., serial port and USB); the northbound ports of the EHM gateways usually use the
Ethernet protocol. Multiple EHM gateways can be connected to the local server via star topology.
The local server, as shown in Figure I.1, has four main functions: firstly, it manages the EHM
gateways and EHM sensors in the community house; secondly, it analyses and stores the EHM data
sent by the EHM sensors; thirdly, it reports the local EHM data to the EHM application server and
IoT platform; fourth, it receives notification from the IoT platform to update the local software.
The EHM application server, as shown in Figure I.1, has two main functions: firstly, it analyses and
storages the EHM data sent by the local server in the community house; secondly, it can share EHM
data, analysis results and computing capability with other EHM application servers.
The IoT platform, as shown in Figure I.1, provides capabilities to facilitate reliability, security, efficient
interworking between the EHM application server and the local server in the community house. Usually
the IoT platform connects with an EHM database which stores and manages EHM data.
I.2 Technical scenario for mobile EHM services
In the mobile EHM services scenario, users usually use a handset (e.g., mobile phone or pad) to access
the EHM services via a wireless network (e.g., cellular network or carrier-WiFi network).
676 Rec. ITU-T Y.4408/Y.2075 (09/2015)