Page 397 - Unleashing the potenti al of the Internet of Things
P. 397
Unleashing the potential of the Internet of Things 4
In SCNs, data can be transmitted via the SCN infrastructure (i.e., using motes and SCN controllers
as intermediate nodes) and via the central communication channel (e.g., using GPRS/3G, Wi-Fi and
WiMAX technologies).
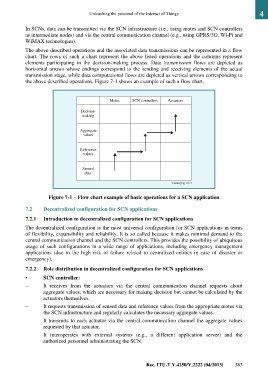
The above-described operations and the associated data transmissions can be represented in a flow
chart. The rows of such a chart represent the above listed operations and the columns represent
elements participating in the decision-making process. Data transmission flows are depicted as
horizontal arrows whose endings correspond to the sending and receiving elements of the actual
transmission stage, while data computational flows are depicted as vertical arrows corresponding to
the above described operations. Figure 7-1 shows an example of such a flow chart.
Motes SCN controllers Actuators
Decision
making
Aggregate
values
Reference
values
Sensed
data
Y.2222(13)_F7-1
Figure 7-1 – Flow chart example of basic operations for a SCN application
7.2 Decentralized configuration for SCN applications
7.2.1 Introduction to decentralized configuration for SCN applications
The decentralized configuration is the most universal configuration for SCN applications in terms
of flexibility, expansibility and reliability. It is so called because it makes minimal demand to the
central communication channel and the SCN controllers. This provides the possibility of ubiquitous
usage of such configurations in a wide range of applications, including emergency management
applications (due to the high risk of failure related to centralized entities in case of disaster or
emergency).
7.2.2 Role distribution in decentralized configuration for SCN applications
• SCN controller:
– It receives from the actuators via the central communication channel requests about
aggregate values, which are necessary for making decision but cannot be calculated by the
actuators themselves.
– It requests transmission of sensed data and reference values from the appropriate motes via
the SCN infrastructure and regularly calculates the necessary aggregate values.
– It transmits to each actuator via the central communication channel the aggregate values
requested by that actuator.
– It interoperates with external systems (e.g., a different application server) and the
authorized personnel administrating the SCN.
Rec. ITU-T Y.4250/Y.2222 (04/2013) 383