Page 155 - Unleashing the potenti al of the Internet of Things
P. 155
Unleashing the potential of the Internet of Things 3
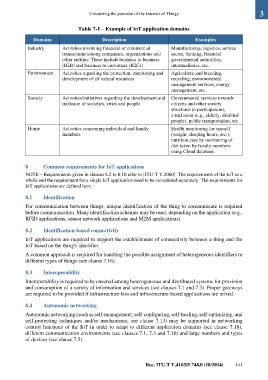
Table 7-1 – Example of IoT application domains
Domains Description Examples
Industry Activities involving financial or commercial Manufacturing, logistics, service
transactions among companies, organizations and sector, banking, financial
other entities: These include business to business governmental authorities,
(B2B) and business to customers (B2Cs) intermediaries, etc.
Environment Activities regarding the protection, monitoring and Agriculture and breeding,
development of all natural resources recycling, environmental
management services, energy
management, etc.
Society Activities/initiatives regarding the development and Governmental services towards
inclusion of societies, cities and people citizens and other society
structures (e-participation),
e-inclusion (e.g., elderly, disabled
people), public transportation, etc.
Home Activities concerning individual and family Health monitoring for oneself
members (weight, sleeping hours, etc.),
nutrition care by monitoring of
diet taken by family members
using Cloud database.
8 Common requirements for IoT applications
NOTE – Requirements given in clauses 8.2 to 8.10 refer to [ITU-T Y.2060]. The requirements of the IoT as a
whole and the requirement for a single IoT application need to be considered separately. The requirements for
IoT applications are defined here.
8.1 Identification
For communication between things, unique identification of the thing to communicate is required
before communication. Many identification schemes may be used, depending on the application (e.g.,
RFID applications, sensor network applications and M2M applications).
8.2 Identification-based connectivity
IoT applications are required to support the establishment of connectivity between a thing and the
IoT based on the thing's identifier.
A common approach is required for handling the possible assignment of heterogeneous identifiers to
different types of things (see clause 7.16).
8.3 Interoperability
Interoperability is required to be ensured among heterogeneous and distributed systems for provision
and consumption of a variety of information and services (see clauses 7.1 and 7.3). Proper gateways
are required to be provided if infrastructure-less and infrastructure-based applications are mixed.
8.4 Autonomic networking
Autonomic networking (such as self-management, self-configuring, self-healing, self-optimizing, and
self-protecting techniques and/or mechanisms; see clause 7.13) may be supported in networking
control functions of the IoT in order to adapt to different application domains (see clause 7.18),
different communication environments (see clauses 7.1, 7.3 and 7.16) and large numbers and types
of devices (see clause 7.5).
Rec. ITU-T Y.4103/F.748.0 (10/2014) 141