Page 102 - Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016
P. 102
3.5.1 Licensing and spectrum management Internet or a telephony network – or directly
over one of these mediums . For consumers, the
76
Licensing and spectrum management are gateway will often be a smart phone or home
important issues for ensuring availability and wireless router. Businesses will frequently use their
capacity for IoT communications. IoT devices existing corporate data networks.
communicate using a range of different protocols,
based on their connectivity requirements and Devices communicating over many kilometres
resource constraints. The protocols include short- need access to the 300 MHz to 3GHz spectrum
range radio protocols such as ZigBee, Bluetooth range, while centimetre or millimetre,
and Wi-Fi, and mobile phone data networks. “contactless” transactions may use near-field
In more specialized applications, such as traffic communications at 13 MHz or in the EHF bands (as
infrastructure, there are longer-range radio shown in Figure 3.6). Some IoT applications may
protocols such as Ultra-Narrow Band (UNB). also make use of AM/FM bands in the VHF range.
Telecommunication companies are experimenting
To communicate with remote networks, IoT with “white space” spectrum to make more use
devices may send data via a gateway with a wired of often-unused spectrum bands, while a US
(PSTN, Ethernet, powerline or DSL) or wireless presidential commission has recommended the
(2G, 3G, 4G/LTE or UNB) connection to the global development of shared-space technology that
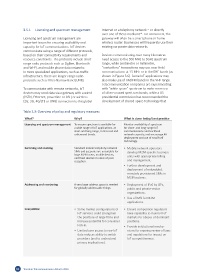
Table 3.3: Overview of policy and regulatory measures
What? Why? What is done today/best practice
Licensing and spectrum management To ensure spectrum is available for Monitor availability of spectrum
a wide range of IoT applications, at for short- and long-range IoT
short and long range, in licensed and communications and backhaul
unlicensed bands. network capacity, and encourage 4G
deployment and use of small-cell
technology.
Switching and roaming Standard mobile telephony network • Mobile network operators
SIMs and accounts are unsuitable for develop M2M-specific business
large M2M users, mobile devices, units with appropriate billing
and fixed devices in areas of poor
reception. and management.
• Further development and
deployment of embedded,
remotely provisioned SIMs in
M2M systems.
Addressing and numbering A very large address space is needed • Deployment of IPv6 by ISPs,
for globally addressable things. public and private-sector
organizations.
• Use of IMSI for M2M
applications.
Competition • Some market configurations of • Ensure competition regulators
IoT services could strengthen have capability to monitor IoT
the positions of large firms and markets for abuses of dominant
increase potential for consumer positions.
lock-in. • Provide institutional mecha-
• Limited user access to raw IoT nisms for ongoing review of laws
data reduces ability to switch and regulations for impact on
providers (and to understand IoT competitiveness.
privacy implications).
84 Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016